Gas welding has always fascinated me. It’s a method that combines heat, precision, and skill to join metals seamlessly. I have worked on numerous welding projects, and gas welding has been one of the most versatile techniques in my toolbox. But what makes it so adaptable? The different types of gas welding methods each bring unique advantages to the table.
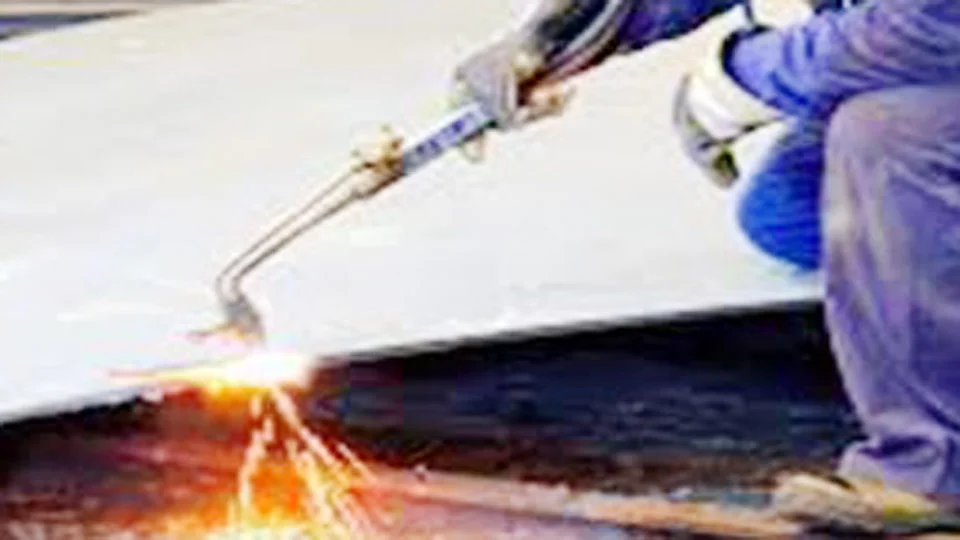

If you’re a seasoned welder or just starting, understanding these types can help you pick the right technique for your project. Let’s dive into the various gas welding methods, their benefits, and where they shine the most.
What Is Gas Welding?
Gas welding is a process where a flame produced by burning a fuel gas with oxygen melts and joins metals. The most common fuel gas used is acetylene, but other gases like propane and hydrogen are also popular depending on the application.
What makes gas welding stand out is its portability and precision. Unlike some modern welding techniques, it doesn’t require electricity, making it an excellent choice for fieldwork or locations without power access.
Different Types of Gas Welding
Here’s a closer look at the main types of gas welding techniques and how they’re used:
Oxy-Acetylene Welding
Oxy-acetylene welding, often referred to as OAW, is one of the most widely used and recognized forms of gas welding. This method uses a combination of oxygen and acetylene to produce a flame hot enough to melt most metals.
Why It’s Popular:
- The flame can reach temperatures up to 6,300°F, making it ideal for heavy-duty projects.
- It’s versatile and works on a variety of metals, including steel, aluminum, and cast iron.
- Perfect for tasks requiring precision, like automotive repairs or jewelry making.
Applications:
I’ve used oxy-acetylene welding for everything from repairing cracked pipes to creating art sculptures. It’s also widely used in industries like manufacturing, plumbing, and shipbuilding.
Advantages:
- High temperature for strong welds.
- Portable and easy to set up.
- Suitable for cutting as well as welding.
Oxy-Hydrogen Welding
Oxy-hydrogen welding is another common type, where hydrogen is used as the fuel gas instead of acetylene. While it doesn’t burn as hot as oxy-acetylene, it’s still effective for certain applications.
Why It’s Unique:
- Produces a flame temperature of around 5,000°F.
- It’s cleaner since hydrogen doesn’t produce soot or carbon deposits.
Applications:
I’ve found this method to be particularly useful for welding thinner metals or working on projects where cleanliness is a priority, such as in the food and beverage industry.
Advantages:
- Cost-effective compared to acetylene.
- Reduced risk of carbon contamination.
- Excellent for delicate and precision work.
Oxy-Propane Welding
Oxy-propane welding uses propane as the fuel gas. While it’s not as hot as acetylene, it’s still a solid option for specific tasks.
Why It’s a Great Alternative:
- Propane is more affordable and easier to store than acetylene.
- While it’s not ideal for welding, it’s excellent for cutting and brazing.
Applications:
This method is widely used in plumbing, HVAC systems, and even decorative metalwork. When I need to cut thick steel plates or join copper pipes, oxy-propane is my go-to choice.
Advantages:
- Affordable fuel source.
- Longer-lasting fuel supply.
- Safer to handle than acetylene.
Air-Acetylene Welding
Unlike other methods that use pure oxygen, air-acetylene welding relies on atmospheric air mixed with acetylene to create the flame.
Why It’s Handy:
- It’s simpler and more portable since it doesn’t require an oxygen cylinder.
- While the flame isn’t as hot, it’s perfect for light-duty tasks.
Applications:
I’ve used air-acetylene welding for soldering and brazing tasks, especially in plumbing and refrigeration work. It’s also great for smaller repairs where precision isn’t as critical.
Advantages:
- Lightweight and portable setup.
- Cost-effective for smaller projects.
- Easy to use, making it ideal for beginners.
Atomic Hydrogen Welding
This is a more specialized type of gas welding that uses hydrogen passed through an arc between two tungsten electrodes. The heat produced melts the metal, allowing it to fuse.
Why It’s Powerful:
- Produces extremely high temperatures, even higher than oxy-acetylene.
- Ideal for welding tungsten, steel, and other high-strength alloys.
Applications:
This method is less common, but it’s used in industries requiring ultra-strong welds, such as aerospace or heavy machinery manufacturing.
Advantages:
- Exceptional heat control.
- Produces clean, high-quality welds.
- Effective on hard-to-weld metals.
Carbon Arc Welding
Carbon arc welding uses an electric arc between a carbon electrode and the workpiece to generate heat. While technically an arc welding process, it’s often categorized alongside gas welding due to its similarities in technique and application.
Why It’s Effective:
- Works well on non-ferrous metals.
- Often used for tasks like brazing and pre-heating.
Applications:
In my experience, carbon arc welding has been a reliable method for repairing cast iron parts and working with copper alloys.
Advantages:
- Affordable and straightforward setup.
- Excellent for non-ferrous metals.
- Produces minimal spatter.
Advantages of Gas Welding
Each type of gas welding has unique benefits, but they all share some common advantages:
- Portability: Gas welding equipment is compact and easy to transport, making it ideal for fieldwork.
- Versatility: You can use gas welding for cutting, brazing, soldering, and welding.
- Precision: Gas welding allows for fine control, which is perfect for detailed or delicate work.
Choosing the Right Type of Gas Welding
When selecting a gas welding method, consider these factors:
- Material Type: Different metals require different temperatures and techniques.
- Project Scale: Smaller projects may benefit from air-acetylene, while heavy-duty work might need oxy-acetylene.
- Budget: Some gases, like propane, are more affordable than acetylene.
- Skill Level: Beginners may find air-acetylene easier to manage, while advanced welders might prefer atomic hydrogen for complex tasks.
Personal Take on Gas Welding
Gas welding has been a game-changer for many of my projects. Its versatility and portability make it one of my favorite welding techniques. While each type has its strengths, oxy-acetylene remains my go-to for its power and flexibility. That said, I’ve learned the importance of matching the method to the job—it’s all about using the right tool for the task.
Conclusion
Gas welding is an incredibly versatile and valuable skill to master. Whether you’re working on small home repairs, industrial projects, or creative metalwork, there’s a gas welding method suited to your needs. Understanding the different types, their benefits, and their applications can help you achieve cleaner, stronger, and more efficient welds.
If you’re new to welding, start with simpler methods like air-acetylene and work your way up to more advanced techniques. And remember, practice makes perfect. Over time, you’ll develop the precision and confidence needed to tackle any welding challenge.
FAQs
What is the most common type of gas welding?
Oxy-acetylene welding is the most common type, thanks to its versatility and ability to handle a wide range of materials.
Can gas welding be used on aluminum?
Yes, but it requires skill and the right technique. Oxy-acetylene welding is commonly used for aluminum.
Which gas is the hottest for welding?
Acetylene produces the hottest flame when combined with oxygen, making it ideal for heavy-duty tasks.
Is gas welding suitable for beginners?
Yes! Methods like air-acetylene are beginner-friendly and great for learning the basics of welding.
How do I ensure safety while gas welding?
Always wear protective gear, ensure proper ventilation, and handle fuel gases carefully to prevent accidents.

Endow Russel the owner chief editor of giftendow.com . I am a mechanical engineer and assign to an local firm with much experience in welding and industrial equipment.