Ultrasonic welding has revolutionized manufacturing with its efficiency, precision, and eco-friendly approach. If you’re someone who’s been exploring modern welding technologies, chances are you’ve come across this term. At its core, ultrasonic welding uses high-frequency vibrations to bond materials, typically plastics or thin metals, without any external heat or adhesives. But what makes this process so effective? The answer lies in the equipment.
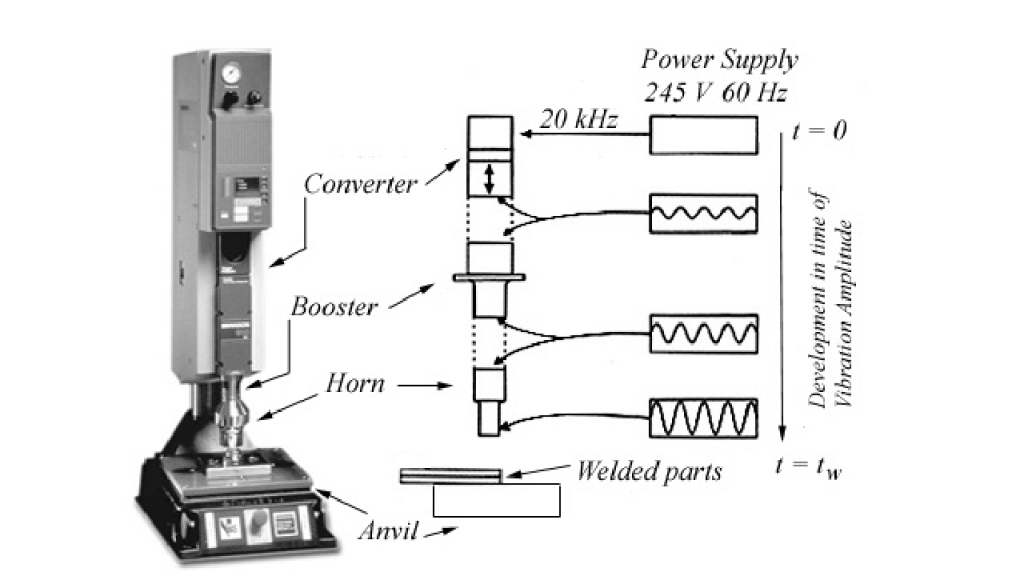
Image by researchgate
I’ll walk you through everything you need to know about ultrasonic welding equipment—how it works, the key components, and what to look for when choosing the right setup for your needs. If you’re in the automotive, electronics, or medical field, this guide will help you understand why ultrasonic welding equipment is a must-have in modern production lines.
Ultrasonic Welding Equipment
If you’ve ever wondered how manufacturers create seamless, strong bonds without using screws, adhesives, or soldering, ultrasonic welding is the answer. Ultrasonic welding equipment is the machinery that enables this high-tech process. It works by converting electrical energy into mechanical vibrations, which are then applied to materials under pressure.
The equipment isn’t just a single machine; it’s a system of components that work in harmony to deliver precision and reliability. From creating electronic circuit boards to manufacturing disposable medical devices, ultrasonic welding equipment is indispensable in industries where speed and quality are critical.
How Ultrasonic Welding Equipment Works
The process begins with the ultrasonic welder converting high-frequency electrical signals into mechanical vibrations using a transducer. These vibrations are transmitted to the materials through a welding horn, which applies pressure to the contact point. The friction from these vibrations generates heat, melting the material at the interface and creating a solid bond.
The beauty of ultrasonic welding is its speed. The entire process often takes less than a second, making it perfect for high-volume production.
Advantages of Ultrasonic Welding Equipment:
- Precision: Welds are accurate and consistent.
- Speed: The process is incredibly fast, increasing production efficiency.
- Eco-Friendly: No adhesives or fillers are needed, reducing waste.
- Versatility: Works on a wide range of materials, including plastics and metals.
Components of Ultrasonic Welding Equipment
Ultrasonic welding equipment consists of several critical components, each playing a unique role in the welding process. Let’s break down these components:
Ultrasonic Generator
The generator is the heart of the ultrasonic welding system. It converts standard electrical power into high-frequency signals (usually 20 kHz to 40 kHz).
Why It’s Important:
- Determines the power and frequency of the welding process.
- Provides the energy needed to create the ultrasonic vibrations.
Transducer
The transducer converts the electrical signals from the generator into mechanical vibrations. This is where electrical energy transforms into the ultrasonic waves that will do the welding.
Key Features:
- Made from piezoelectric materials that generate vibrations when electricity is applied.
- Ensures efficient energy conversion.
Booster
The booster amplifies the mechanical vibrations from the transducer before they reach the welding horn.
Functionality:
- Increases or decreases the amplitude of vibrations, depending on the material being welded.
Welding Horn (Sonotrode)
The horn is the part of the machine that directly contacts the materials being welded. It transmits the vibrations to the materials and applies pressure.
Characteristics:
- Customizable shapes and sizes to suit different applications.
- Typically made of titanium or aluminum for durability.
Fixture (Anvil)
The fixture holds the materials in place during welding. It ensures alignment and stability for precise welds.
Why It’s Essential:
- Prevents material movement during the process.
- Allows for consistent weld quality.
Control Unit
The control unit manages the entire process, allowing operators to adjust parameters like pressure, amplitude, and welding time.
Importance:
- Ensures repeatability and precision.
- Offers real-time monitoring and feedback.
Here’s a table summarizing the components and their functions:
| Component | Function |
|---|---|
| Ultrasonic Generator | Converts electrical power into high-frequency signals |
| Transducer | Converts electrical signals into mechanical vibrations |
| Booster | Amplifies or reduces vibration amplitude |
| Welding Horn | Transmits vibrations to the materials |
| Fixture | Holds materials in place during welding |
| Control Unit | Manages process parameters and monitors performance |
Choosing the Right Ultrasonic Welding Equipment
When selecting ultrasonic welding equipment, it’s important to consider your specific application. Here are a few factors to keep in mind:
Material Compatibility
Not all materials are suitable for ultrasonic welding. Plastics with similar melting points, such as ABS and acrylic, work well. For metals, the materials should be thin and conductive.
Power and Frequency Requirements
The power and frequency of the equipment determine its suitability for different materials and applications. For example:
- Low Frequency (15-20 kHz): Ideal for welding thick materials.
- High Frequency (35-40 kHz): Best for delicate or thin materials.
Customization Options
Look for equipment with customizable welding horns and fixtures to accommodate different shapes and sizes of materials.
Automation Capabilities
If you’re running a high-volume production line, consider ultrasonic welding systems that integrate with automated machinery for seamless operation.
User-Friendly Controls
Ensure the control unit offers intuitive settings and real-time feedback to minimize errors and maximize productivity.
Applications of Ultrasonic Welding Equipment
Ultrasonic welding is a versatile process used across various industries. Here are some common applications:
Automotive Industry
- Welding plastic parts like dashboards, door panels, and bumpers.
- Assembling electronic components, such as sensors and wiring harnesses.
Electronics Industry
- Creating strong bonds in circuit boards, battery casings, and connectors.
- Ensuring precise alignment and minimal distortion in sensitive components.
Medical Devices
- Manufacturing disposable items like surgical instruments, catheters, and IV bags.
- Ensuring hygienic, contamination-free welds.
Packaging Industry
- Sealing food and beverage containers.
- Welding blister packs and other flexible packaging materials.
Aerospace Industry
- Joining lightweight components to reduce overall weight.
- Ensuring high-strength, reliable bonds in critical assemblies.
Advantages of Ultrasonic Welding Equipment
- Eco-Friendly: Eliminates the need for adhesives or fillers, reducing waste.
- Cost-Effective: High efficiency and low material usage translate to lower production costs.
- Versatile: Works on a variety of materials and shapes.
- Precise: Delivers consistent, high-quality welds.
- Fast: Speeds up production cycles, especially in automated setups.
Conclusion
Ultrasonic welding equipment is a game-changer for industries that demand precision, speed, and sustainability. Its ability to create strong, clean bonds without using additional materials makes it a preferred choice for manufacturers worldwide. Whether you’re assembling intricate electronic components or large automotive parts, ultrasonic welding equipment ensures reliability and efficiency.
If you’re considering investing in this technology, take the time to evaluate your specific needs and choose equipment that aligns with your production goals. With the right setup, you’ll not only improve the quality of your products but also streamline your operations.
FAQs
What materials can be welded with ultrasonic welding equipment?
Ultrasonic welding works best with thermoplastics and thin, conductive metals.
Is ultrasonic welding environmentally friendly?
Yes, it doesn’t require adhesives or fillers, making it a sustainable choice.
How fast is the ultrasonic welding process?
The process typically takes less than a second, making it ideal for high-volume production.
Can ultrasonic welding equipment be automated?
Absolutely! Many systems integrate seamlessly with automated production lines.
What industries benefit the most from ultrasonic welding?
Automotive, electronics, medical devices, packaging, and aerospace industries rely heavily on ultrasonic welding.

Endow Russel the owner chief editor of giftendow.com . I am a mechanical engineer and assign to an local firm with much experience in welding and industrial equipment.

