Finding the best welding process for thick metal can be challenging. The right technique ensures strong, durable joints and efficient work.
Thick metals require specific welding methods due to their density and heat conductivity. Choosing the right process is essential for achieving optimal results, whether you are working on construction projects, heavy machinery, or industrial equipment. This guide will explore the most effective welding processes for thick metal, ensuring you have the knowledge to select the best approach.
By understanding the unique benefits and applications of each method, you can make informed decisions that enhance your welding projects. Let’s dive into the options and find the perfect technique for your needs.
Introduction To Welding Thick Metal
Welding thick metal is not for the faint-hearted. It’s a skill that requires precision, patience, and the right technique. Whether you’re a seasoned welder or a newbie, understanding the intricacies of welding thick metal can make the difference between a sturdy structure and a flimsy one.
Welding thick metal is a different ball game compared to thinner sheets. The thicker the metal, the more challenging it becomes to ensure a strong, durable bond. This process is essential in construction, shipbuilding, and heavy machinery, where the strength of the weld is critical. But why is the technique so important, and what are the common challenges faced by welders? Let’s dive in.
Importance Of Technique
Using the right technique for welding thick metal is crucial. You can’t just slap on a weld and hope for the best. Here are a few reasons why technique matters:
- Structural Integrity: Proper technique ensures that the weld will hold up under stress.
- Safety: A strong weld prevents accidents and equipment failure.
- Efficiency: Good technique can save time and materials.
Imagine trying to build a bridge with poor welding techniques. It’s a recipe for disaster, right? That’s why mastering the correct method is key.
Challenges Faced
Welding thick metal comes with its own set of hurdles. Here are some common challenges:
- Heat Management: Thick metal requires more heat, which can lead to warping or weakening if not handled correctly.
- Penetration: Ensuring the weld penetrates deep enough to fuse the metal properly is tricky.
- Positioning: Handling large, heavy pieces of metal is physically demanding and requires careful planning.
Let’s not forget the sheer physical effort involved. Ever tried holding a welding torch steady for hours on end? It’s like an arm workout from hell!
But fear not! With the right knowledge and practice, these challenges can be overcome, leading to strong, reliable welds that stand the test of time.

Credit: unimig.com.au
Choosing The Right Welding Process
Choosing the right welding process for thick metal is crucial. Different methods suit different needs. The right choice ensures strong, durable welds. A poor choice can lead to weak bonds. These can compromise safety and performance. Consider several key factors to make the best decision.
Factors To Consider
First, think about the thickness of the metal. Thick metals need more heat. This affects the type of welding process. Next, consider the type of metal. Some metals need special techniques. Finally, look at the position of the weld. Some methods work better in tight spaces. Others need more room to move.
Popular Welding Methods
Several welding methods are popular for thick metal. MIG welding is one. It is known for speed and ease. TIG welding is another. It offers precision and clean welds. Stick welding is also common. It is effective for thick sections. Each method has its strengths. Choose the one that fits your needs best.
Shielded Metal Arc Welding (smaw)
When it comes to welding thick metal, one technique stands out for its versatility and reliability: Shielded Metal Arc Welding (SMAW). Also known as stick welding, SMAW is a manual process that uses a consumable electrode coated with flux to lay the weld. It’s perfect for working with heavy-duty metals and is widely used in various industries, from construction to shipbuilding. Let’s dive into why SMAW is a top choice for thick metal welding.
Advantages
SMAW offers several benefits that make it a preferred method for welding thick metal:
- Versatility: SMAW can weld various metals, including steel, stainless steel, and cast iron. This makes it a flexible choice for different projects.
- Cost-Effective: The equipment and materials required for SMAW are relatively inexpensive compared to other welding processes.
- Portability: The equipment is easy to transport, making it ideal for fieldwork and remote locations.
- Strong Welds: SMAW produces strong and durable welds, capable of withstanding heavy stress and harsh environments.
Best Practices
To achieve the best results with SMAW, it’s crucial to follow some best practices:
- Electrode Selection: Choose the right electrode for the metal type and thickness. For thick metals, E7018 electrodes are often recommended due to their deep penetration and strong welds.
- Proper Preparation: Clean the metal surface thoroughly to remove any rust, dirt, or oil. This ensures better adhesion and prevents weld contamination.
- Correct Settings: Adjust the welding machine to the appropriate current and voltage settings based on the electrode and metal thickness.
- Consistent Technique: Maintain a steady hand and consistent travel speed. This helps produce uniform weld beads and prevents defects.
- Safety First: Always wear appropriate protective gear, including a welding helmet, gloves, and flame-resistant clothing. Safety should never be compromised.
In conclusion, SMAW is an excellent choice for welding thick metal. Its advantages and straightforward best practices make it accessible for both beginners and experienced welders. So, next time you’re faced with a hefty welding project, consider giving SMAW a try. You might just find it’s the perfect fit for your needs!
Gas Metal Arc Welding (gmaw)
When it comes to welding thick metal, Gas Metal Arc Welding (GMAW) is a strong contender. Also known as MIG (Metal Inert Gas) welding, GMAW is popular for its versatility and ease of use. This welding process involves feeding a continuous wire electrode through a gun, while an inert gas shields the weld pool from contamination. Let’s dive into why GMAW is a top choice for thick metal welding and some handy tips to get the best results.
Benefits
GMAW offers numerous advantages that make it a preferred method for welding thick metals. Here are some key benefits:
- High Welding Speed: GMAW allows for faster welding compared to other methods, which can save time, especially on large projects.
- Cleaner Welds: The inert gas used in GMAW helps produce clean, high-quality welds with minimal spatter.
- Ease of Use: GMAW is relatively easy to learn and use, making it accessible even for beginners.
- Versatility: This method can be used on a variety of metals including carbon steel, stainless steel, and aluminum.
Application Tips
To ensure the best results with GMAW, consider the following application tips:
- Choose the Right Wire: Using the correct wire type and size for your specific metal is crucial. For thicker metals, a larger diameter wire is usually preferred.
- Adjust the Settings: Ensure your welding machine settings are properly adjusted for the thickness of the metal. This includes voltage, wire feed speed, and gas flow rate.
- Maintain a Steady Hand: Keeping a steady hand and consistent speed helps create uniform welds. Practice makes perfect!
- Use Proper Shielding Gas: The choice of shielding gas can affect the quality of your weld. For example, a mix of argon and carbon dioxide is often used for steel.
- Clean the Metal: Always clean the metal surface before welding to remove rust, paint, or other contaminants that can affect the weld.
By following these tips, you can leverage the benefits of GMAW to achieve strong, clean welds on thick metal. Whether you’re a seasoned welder or just starting, GMAW can make your welding projects easier and more efficient. So, ready to spark up that welding torch and get to work?
Flux-cored Arc Welding (fcaw)
Flux-Cored Arc Welding (FCAW) is a popular method for welding thick metal. It is effective and efficient. FCAW uses a tubular wire filled with flux. This wire helps shield the weld from contaminants. The process is similar to MIG welding but has its own advantages. FCAW is versatile and works well in various environments.
When To Use
FCAW is ideal for welding thick metal. It is suitable for heavy-duty tasks. Use it in construction, shipbuilding, and heavy equipment repair. This process is effective even in windy conditions. It also works well on dirty or rusty metals. Choose FCAW for outdoor projects and industrial applications.
Technical Guidelines
Follow specific guidelines for successful FCAW. First, select the right wire type. There are two main types: self-shielded and gas-shielded. Self-shielded wires are best for outdoor use. Gas-shielded wires offer cleaner welds. Next, adjust the voltage and wire feed speed. These settings depend on the metal thickness. Ensure proper polarity settings. Use DC positive for most applications.
Maintain a clean work area. Remove rust, paint, and debris before welding. Use proper safety gear. Wear gloves, a helmet, and protective clothing. Ensure good ventilation in your workspace. Follow these guidelines for effective and safe welding.
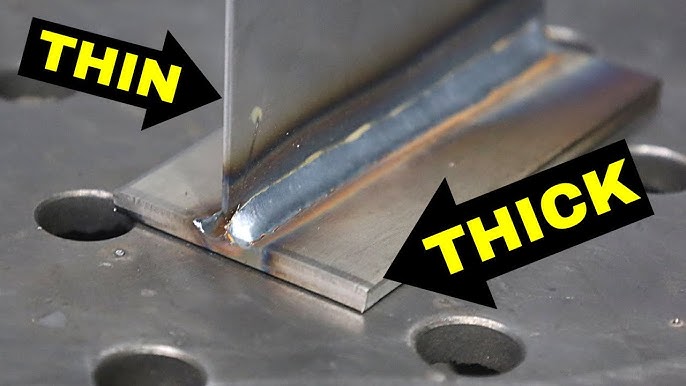
Credit: www.youtube.com
Submerged Arc Welding (saw)
Submerged Arc Welding (SAW) is a popular welding method. It uses a continuous wire electrode and a granular flux. This welding process is known for its high efficiency and deep penetration. SAW is widely used in industries for heavy-duty welding tasks.
Suitability For Thick Metal
SAW is ideal for welding thick metal. It provides deep penetration, ensuring strong welds. The process handles high currents, making it perfect for thick sections. SAW also offers a high deposition rate, reducing welding time.
Operational Techniques
SAW requires a clean work surface. Remove rust, oil, and dirt before welding. Use a continuous wire electrode for consistent weld quality. The granular flux covers the arc, protecting it from contamination. This improves weld quality and reduces spatter.
The welding speed can be adjusted based on the metal thickness. For thicker metals, a slower speed allows deeper penetration. Automated SAW systems enhance precision and efficiency. They provide consistent welds, even for large projects.
Preparation And Safety
Welding thick metal requires careful preparation and strict safety measures. Proper preparation ensures a strong weld. Safety measures protect the welder and others. Both steps are crucial for a successful welding project. Let’s dive into the details.
Material Preparation
First, clean the metal surface. Remove rust, paint, and dirt. Use a wire brush or grinder. A clean surface ensures a strong weld. Next, preheat the metal. Thick metal needs preheating to avoid cracks. Use a torch or oven for this step. Measure the temperature with a thermometer. Follow the recommended preheating temperature for your metal type.
Check the fit-up of the metal pieces. Ensure they align properly. Use clamps to hold the pieces in place. A good fit-up ensures a strong joint. Mark the welding area. Use chalk or a marker. This helps you stay on track while welding.
Protective Measures
Wear protective gear. This includes a welding helmet, gloves, and a jacket. The helmet protects your eyes from sparks and bright light. Gloves protect your hands from burns. The jacket protects your body from hot metal.
Ensure proper ventilation. Welding produces harmful fumes. Work in a well-ventilated area. Use an exhaust fan if needed. Keep a fire extinguisher nearby. Welding sparks can cause fires. Be ready to put out any flames.
Secure the work area. Remove flammable materials. Keep your workspace clean. This reduces the risk of accidents. Inform others about your welding. Ensure they stay at a safe distance.

Credit: yeswelder.com
Expert Tips For Successful Welding
Welding thick metal requires precision and expertise. Knowing the best practices can make a significant difference. This section offers expert tips to ensure your welding projects are successful. Whether you are new or experienced, these tips will help improve your welds.
Common Mistakes To Avoid
Many welders make avoidable errors. One common mistake is not cleaning the metal properly. Dirt and rust can weaken the weld. Another mistake is using the wrong welding technique. Each technique suits different metals and thicknesses. Also, avoid rushing the welding process. Take your time to ensure strong and lasting welds.
Enhancing Weld Quality
Quality welds start with the right tools. Invest in a good welding machine. Also, use the correct filler material for the metal type. Preheating the metal can help with thicker pieces. It reduces the risk of cracks. Practice makes perfect, so keep honing your skills. Clean your equipment regularly to maintain performance. Lastly, always inspect your welds thoroughly. Look for any signs of defects or weak spots.
Frequently Asked Questions
Which Welding Is Best For Thick Metal?
The best welding for thick metal is flux-cored arc welding (FCAW). It penetrates deeply and handles heavy-duty projects effectively.
Is Mig Or Tig Better For Thick Metal?
MIG welding is generally better for thick metal due to its deep penetration and faster welding speed. TIG welding offers precision but is slower. For thick materials, MIG is the preferred choice.
How To Weld Thick Metal?
To weld thick metal, use a high-amperage welder. Preheat the metal to reduce thermal stress. Apply multiple welding passes. Use proper filler material. Ensure adequate cooling time.
Which Welding Is Used For Heavy Metals?
TIG and MIG welding are used for heavy metals. They provide strong, precise welds suitable for thick materials.
Conclusion
Choosing the best welding process for thick metal is crucial. MIG, TIG, and Stick welding offer different benefits. Each method has its own strengths. MIG welding is fast and efficient. TIG welding provides precision and control. Stick welding works well outdoors and on rusty surfaces.
Consider your project’s needs. Match the welding process to your specific requirements. This way, you’ll achieve strong, durable welds. Your project will be successful with the right welding choice. Happy welding!

