Welding is a fascinating process. It joins materials, typically metals, by melting and fusing them.
In welding, heat is applied to metal pieces to melt and fuse them. This creates a strong bond. Different techniques exist, each suited for specific tasks. Understanding how welding works can help you appreciate its role in construction and manufacturing.
From building bridges to crafting art, welding is essential. It’s not just about joining metal; it’s about precision and skill. With the right knowledge, welding becomes more than just sparks and flame. It becomes an art form, creating robust and lasting structures. Ready to dive deeper? Let’s explore the world of welding and see how it all comes together.
Credit: info.naimormetalfabrication.com
Introduction To Welding
Have you ever wondered how metal pieces are joined together? Whether it’s in a car, a bridge, or even a small sculpture, welding is the hero behind the scenes. Welding is a fascinating process that involves joining materials, usually metals or thermoplastics, by causing coalescence. It’s like creating a strong bond that holds everything together. But how exactly does it work? Let’s dive in!
Importance Of Welding
Welding is crucial in many industries. Think about it – without welding, many structures we rely on wouldn’t exist. Consider the construction of buildings, ships, and even airplanes. Welding ensures these structures are solid and safe. It’s not just about sticking pieces together; it’s about creating something reliable and durable.
Here’s why welding is so important:
- Strength: Welded joints are often stronger than the materials being joined.
- Efficiency: Welding can be faster and more efficient than other joining methods.
- Versatility: It can be used on various materials and shapes.
Common Applications
Welding is everywhere! From the smallest gadgets to the largest constructions, welding plays a key role. Here are some common applications:
| Industry | Application |
|---|---|
| Automotive | Cars, Trucks, Motorcycles |
| Construction | Buildings, Bridges, Infrastructure |
| Manufacturing | Machinery, Equipment, Tools |
| Art | Sculptures, Metal Art, Decor |
Picture this: you’re driving your car on a highway. Every part of that car – from the frame to the engine – has been touched by welding. Or imagine standing on a bridge, enjoying the view. Without welding, that bridge wouldn’t be there. Amazing, right?
Welding is not just a technical skill; it’s an art. It requires precision, patience, and practice. So, the next time you see a welder at work, remember the magic they’re creating, one spark at a time.
Credit: weldguru.com
Types Of Welding Processes
Welding is a crucial skill in many industries. It involves joining metals together by melting them. There are several welding processes, each suited to different applications. Understanding these types can help you choose the right one for your project.
Arc Welding
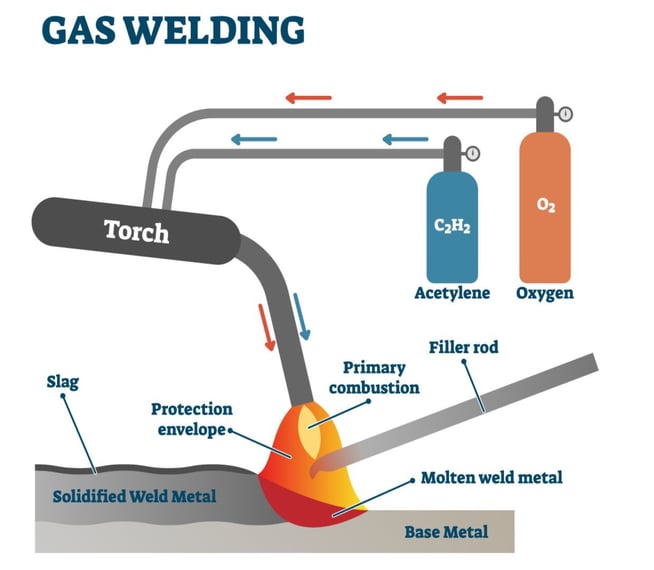
Arc welding uses an electrical arc to melt metals at the weld point. This process is versatile and works with many metals. It is commonly used in construction and repair work. The heat from the arc melts the metal, which then cools and solidifies to form a strong bond.
Mig Welding
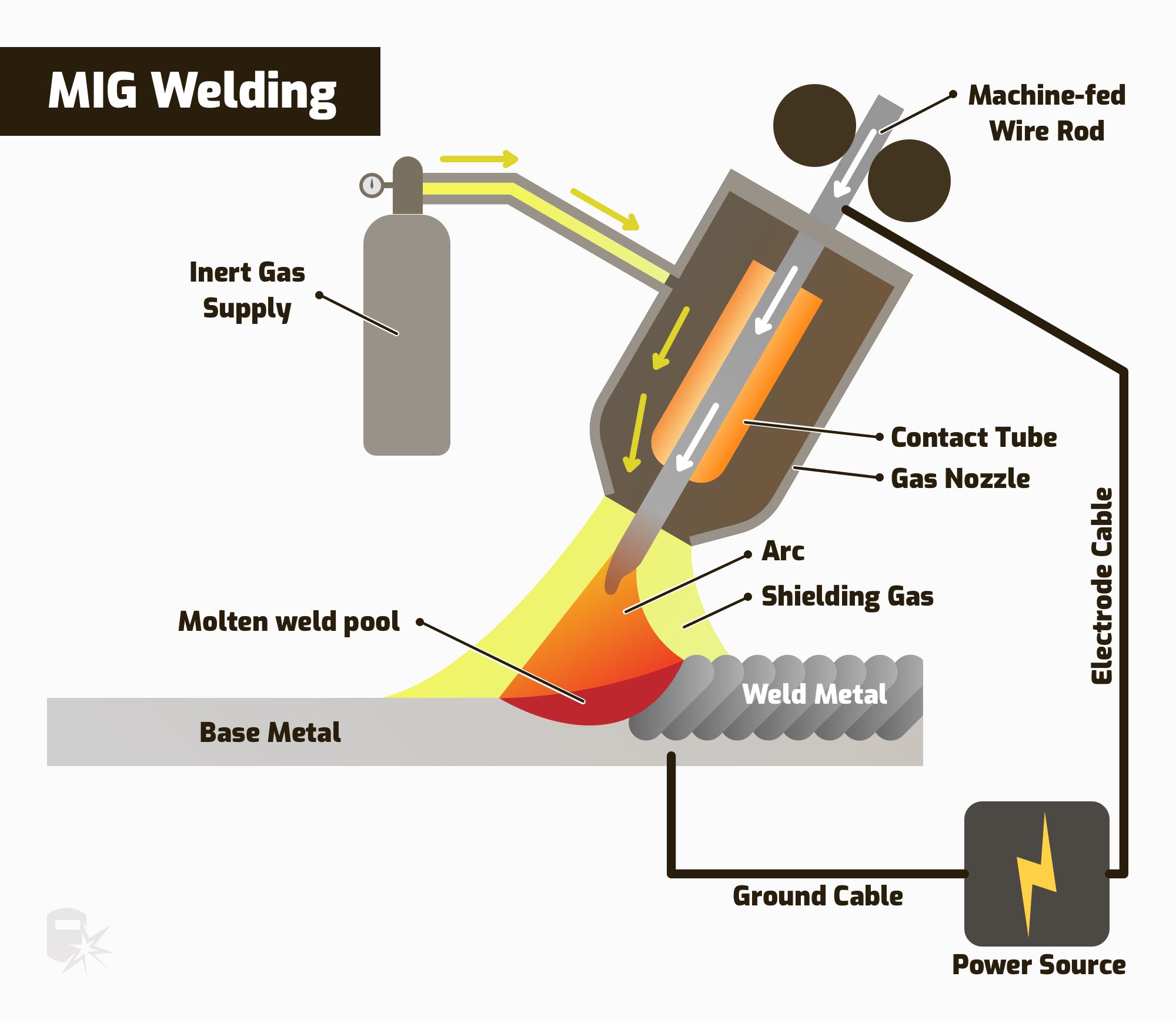
MIG welding, or Metal Inert Gas welding, uses a continuous wire feed. The wire acts as both an electrode and filler material. A shielding gas protects the weld from contamination. This method is fast and efficient. It is ideal for welding thin to medium-thickness metals.
Tig Welding
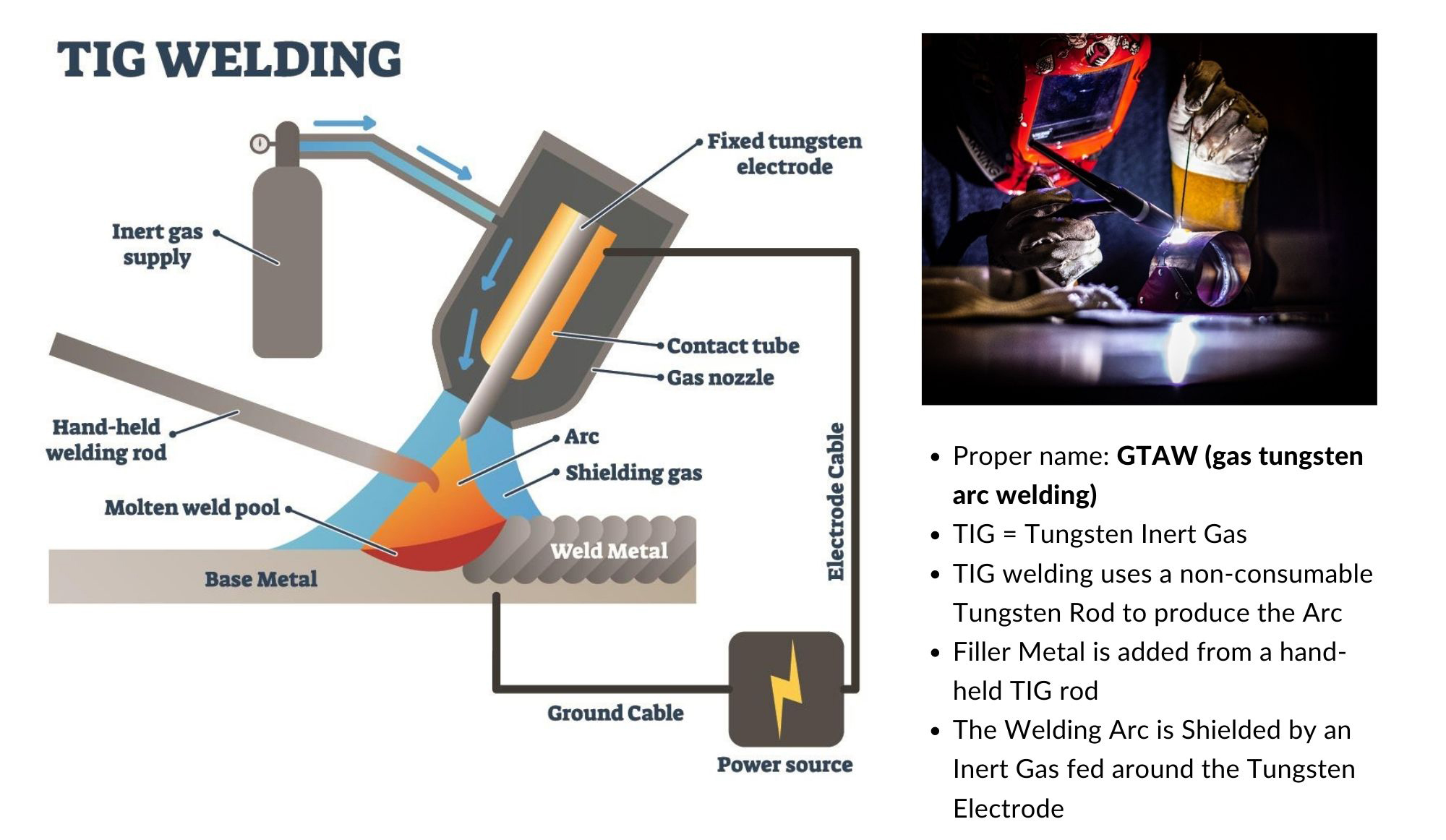
TIG welding stands for Tungsten Inert Gas welding. It uses a tungsten electrode to produce the weld. A separate filler material can be added by hand. The process is precise and clean. It works well with thin materials and high-quality welds.
Resistance Welding
Resistance welding uses pressure and electric current to join metals. The current passes through the metal pieces, generating heat. This heat causes the metal to melt and fuse together. It is often used in manufacturing and automotive industries. The process is fast and produces minimal distortion.
Materials Used In Welding
Welding joins materials by melting and fusing them together. Different materials require different techniques. Here, we will explore the main materials used in welding.
Metals
Metals are the most common materials in welding. Steel is often used due to its strength and versatility. Stainless steel resists rust and corrosion, making it ideal for many projects. Aluminum is lightweight and resistant to corrosion, perfect for aircraft and automotive parts. Copper and titanium are also used in specialized welding applications.
Non-metals
Non-metals are used in welding, but less frequently than metals. Plastics can be welded using different methods like ultrasonic welding. Ceramics, due to their high melting points, require special techniques like laser welding. These materials are used in various industries, including electronics and medical devices.
Alloys
Alloys are mixtures of two or more elements, usually metals. They provide enhanced properties like strength, durability, and resistance to wear. Common alloys in welding include brass, bronze, and nickel alloys. Each alloy has unique characteristics that make it suitable for specific applications. Welding alloys often require special techniques to maintain their properties.
The Physics Of Welding
Welding is an incredible process where metal pieces are fused together to create everything from skyscrapers to sculptures. But how does it all come together? Let’s dive into the physics of welding and uncover the magic behind the sparks.
Heat Generation
Have you ever watched a blacksmith work? They heat the metal until it’s red-hot. Similarly, in welding, heat is essential. Different methods like arc welding use electricity, while others might use gas. This heat is intense, often reaching thousands of degrees. It’s what makes the metal pliable.
Melting And Fusion
Once the metal is hot enough, it starts to melt. Imagine ice cubes turning into water; that’s similar to what happens with metal during welding. The molten metal from the two pieces mixes and forms a pool. This pool is where the magic happens. It’s where the two separate pieces become one. Think of it as making a friendship bracelet where the threads are intertwined.
Cooling And Solidification
After the metal pieces have fused, they need to cool down. This is like waiting for a cake to set after it’s been baked. As the metal cools, it becomes solid again. But this isn’t just any solid metal; it’s now a strong, unified piece. The cooling process must be controlled to avoid cracks or weaknesses.
So, there you have it! The physics of welding is about heating, melting, and cooling metal to create strong connections. Whether you’re building a bridge or fixing a bike, understanding these basics can help you appreciate the art and science behind welding.
Welding Equipment And Tools
Welding is a fascinating process that joins materials, usually metals or thermoplastics, by causing coalescence. But, have you ever wondered what kind of equipment and tools are used to achieve those seamless joins? Let’s dive into the essential gear that makes welding possible and effective.
Welding Machines
Welding machines are the heart of any welding operation. They come in various types, each suited for different welding techniques. The common ones include:
- MIG Welders: These are user-friendly and perfect for beginners. They use a wire feeding gun to create the weld.
- TIG Welders: Ideal for precision work, TIG welders use a tungsten electrode to produce the weld.
- Stick Welders: Also known as Shielded Metal Arc Welding (SMAW) machines, these are great for outdoor work due to their robustness.
Choosing the right welding machine depends on your project needs and skill level. When I started, a MIG welder was my go-to because it was easy to handle and forgiving with mistakes.
Safety Gear
Safety is paramount in welding. The bright light and high temperatures can be hazardous. Here’s a list of essential safety gear:
- Welding Helmet: Protects your eyes and face from sparks and harmful radiation. Auto-darkening helmets are a popular choice.
- Gloves: Heavy-duty gloves shield your hands from heat and electrical shocks.
- Protective Clothing: Fire-resistant jackets and aprons are a must to prevent burns.
- Safety Glasses: Wear these under your helmet for extra eye protection.
Think of safety gear as your armor. Just like you wouldn’t go into battle unprepared, don’t start welding without the proper protection. Trust me, a small spark can cause a big injury.
Filler Materials
Filler materials are what you use to fill the gap between the two pieces being welded. The type of filler material used can significantly affect the strength and quality of the weld. Here are some common fillers:
- Welding Rods: These are used in Stick welding. They come coated with flux to protect the weld area from contamination.
- Welding Wire: Used in MIG welding, this wire is fed through the welding gun and melts to form the weld.
- TIG Filler Rods: These are used in TIG welding and are manually fed into the weld pool.
Choosing the right filler material can be a bit like selecting the right seasoning for your food. Too much or too little can make a big difference. When I first started welding, I experimented with different rods and wires to find what worked best for different metals.
In conclusion, understanding the equipment and tools of welding is crucial to getting started. Whether you’re a beginner or looking to improve your skills, knowing your gear can make all the difference. So, gear up, stay safe, and happy welding!
Credit: info.naimormetalfabrication.com
Welding Techniques
Welding is a fascinating process that joins materials together by melting them. It’s like magic for metal! But how exactly does it work? There are several techniques that welders use to get the job done. Let’s dive into some key aspects of these techniques.
Joint Preparation
Before you start welding, you need to prepare the joint. This means cleaning the surfaces and making sure they fit together well. Think of it like making a sandwich. You wouldn’t put peanut butter on dirty bread, right? Here are some steps:
- Clean the Surface: Remove rust, paint, and dirt.
- Fit-Up: Make sure the pieces align perfectly.
- Tack Welding: Use small welds to hold pieces in place.
Proper joint preparation ensures a strong weld. Skip this step, and you’re asking for trouble!
Welding Positions
Welding isn’t always done on a flat table. Sometimes you have to weld in tricky spots. Here are some common welding positions:
| Position | Description |
|---|---|
| Flat | Welding on a horizontal surface. |
| Horizontal | Welding on a vertical surface, but the weld line is horizontal. |
| Vertical | Welding up or down a vertical surface. |
| Overhead | Welding from below the joint. |
Each position has its challenges. Imagine trying to write on a wall versus a desk. That’s the difference!
Welding Speed
Welding speed is crucial. Too fast, and the weld might be weak. Too slow, and you could burn through the material. It’s like cooking pasta. Boil it too long, and it’s mushy; too short, and it’s crunchy.
- Consistent Speed: Keep a steady pace for an even weld.
- Practice: The more you weld, the better you get at controlling speed.
- Equipment Settings: Adjust your welder to match the material and thickness.
Finding the right speed takes practice, but it’s key to making strong, clean welds.
Welding is both an art and a science. By understanding joint preparation, welding positions, and welding speed, you can improve your skills and make better welds. Remember, even the best welders were beginners once. So, don’t get discouraged and keep practicing!
Safety In Welding
Welding is a fascinating process, but it can be dangerous if the proper precautions are not taken. Safety in welding is crucial to protect yourself and others from potential hazards like burns, electric shock, and harmful fumes. Let’s dive into some important aspects of welding safety.
Protective Clothing
Wearing the right clothes is essential when welding. It’s not just about looking cool in a helmet! You need to shield your skin from sparks and hot metal. Here’s what you should wear:
- Helmet: A welding helmet with a proper filter shade protects your eyes and face.
- Gloves: Heavy-duty leather gloves keep your hands safe from heat and sharp metal.
- Jacket: A flame-resistant jacket prevents burns. It should cover your arms completely.
- Pants: Wear long pants made of sturdy material like denim. No shorts allowed!
- Boots: Leather boots with steel toes protect your feet from falling objects.
Ventilation
Welding produces fumes that can be harmful if inhaled. Good ventilation is a must to keep the air clean. Here are some tips:
- Work in a well-ventilated area. Open windows and doors if possible.
- Use exhaust fans to remove fumes from the workspace.
- Wear a respirator mask if you’re working in a confined space.
- Keep your head out of the direct path of the fumes. Position yourself to the side.
Remember, safety first! Inhaling fumes can cause serious health issues.
Fire Prevention
Welding involves high temperatures, which means there’s always a risk of fire. Here’s how to prevent it:
- Clear the Area: Remove any flammable materials like paper, wood, and gasoline from your workspace.
- Have a Fire Extinguisher: Keep a fire extinguisher nearby. Make sure you know how to use it.
- Watch for Sparks: Sparks can fly several feet. Ensure your work area is free of anything that might catch fire.
- Check Equipment: Regularly inspect your welding equipment for damage. Faulty gear can cause sparks and fires.
It’s better to be safe than sorry. Always keep an eye out for potential fire hazards.
In conclusion, safety in welding is not something to take lightly. By wearing protective clothing, ensuring proper ventilation, and preventing fires, you can enjoy welding while keeping yourself and others safe. After all, nobody wants their amazing welding project to turn into a trip to the emergency room, right?
Common Welding Challenges
Welding is an art, a science, and a skill all rolled into one. But like any craft, it comes with its fair share of challenges. Whether you’re a seasoned welder or just starting, knowing the common pitfalls can save you time and frustration. Let’s dive into some of the most frequent welding challenges and how to tackle them.
Cracks And Porosity
Ever wondered why some welds end up looking like a piece of Swiss cheese? That’s porosity for you. Porosity occurs when gas gets trapped in the weld pool, leaving holes. Cracks, on the other hand, happen when there’s too much stress on the weld. Both issues can weaken your weld, making it less durable.
Tips to avoid cracks and porosity:
- Keep your materials clean. Dirt and oil can introduce gases into the weld.
- Control your welding speed. Too fast or too slow can cause issues.
- Use the right filler material. Mismatched materials can lead to cracks.
Distortion
Distortion is like trying to bake a perfect cake and ending up with a lopsided mess. It happens when the metal expands and contracts unevenly during welding. The result? A warped piece that’s far from what you intended.
Ways to reduce distortion:
- Use clamps to hold your workpiece in place.
- Weld in short sections to minimize heat buildup.
- Allow the metal to cool between passes.
Incomplete Fusion
Incomplete fusion is like making a sandwich but forgetting to add the filling. It occurs when the weld metal doesn’t fully fuse with the base metal, leading to weak spots. This can compromise the strength and integrity of the weld.
How to ensure complete fusion:
- Maintain proper heat. Too low, and the metals won’t meld.
- Ensure good access. Awkward angles can prevent thorough welding.
- Use the right technique. Consistent motion helps achieve full fusion.
Welding might seem daunting with these challenges, but remember: every welder started somewhere. By understanding and addressing these common issues, you can improve your skills and create strong, reliable welds. Happy welding!
Advancements In Welding Technology
Welding has come a long way from its early days. New technologies are transforming the field. These advancements make welding faster, safer, and more precise. Let’s explore some of these exciting developments.
Automation In Welding
Automation has changed the welding industry. Machines now handle tasks that used to need human hands. This reduces errors and speeds up production. Automated welding systems are becoming more common in factories. They can work non-stop and don’t get tired. This means higher efficiency and less downtime.
Laser Welding
Laser welding is another major advancement. It uses a focused beam of light to join materials. The beam heats the materials until they melt and fuse together. This method is very precise. It’s perfect for delicate or detailed work. Laser welding is also fast. It can join metals in seconds. This makes it ideal for industries like aerospace and electronics.
Robotic Welding
Robotic welding is the use of robots in welding. These robots can perform complex welding tasks with ease. They are programmable and can repeat tasks with great accuracy. This technology is used in car manufacturing and construction. Robotic welding is reliable. It reduces the need for skilled welders in repetitive tasks. This allows human workers to focus on more creative and complex projects.
Frequently Asked Questions
How Does The Welding Process Work?
The welding process joins materials by melting their edges with high heat. A filler material is added to form a strong joint. This process often uses a protective gas to shield the weld from contaminants. Welding methods include MIG, TIG, and arc welding, each suited for different materials and applications.
What Actually Happens When Welding?
Welding joins materials by melting them with high heat. The molten sections cool and solidify, forming a strong bond. Various techniques, like MIG, TIG, and arc welding, suit different materials and applications. Proper safety gear is essential during the process.
How Are Welds So Strong?
Welds are strong because they fuse two materials together, creating a continuous bond. This bond distributes stress evenly. Quality welds use proper techniques and materials, ensuring durability and strength.
Is Welding Just Melting Metal Together?
No, welding involves more than just melting metal. It joins materials by heating, applying pressure, or both. Different techniques and processes ensure strong and durable connections.
Conclusion
Welding is a fascinating and essential skill. It joins metals together. Different welding methods suit various needs. Safety measures are crucial for welders. Proper training makes welding effective and safe. Always use the right equipment. Remember, practice improves your welding skills.
Now, you understand how welding works. Try learning more and practicing it safely. Happy welding!

