Welding galvanized steel can be tricky and dangerous. The process releases toxic fumes.
Galvanized steel is coated with a layer of zinc to prevent rust. When welded, this zinc coating melts and produces harmful zinc oxide fumes. These fumes can cause serious health problems, like metal fume fever. Understanding the risks and safety measures when welding galvanized steel is crucial.
In this blog post, we will explore what happens during the welding process, why it’s risky, and how to stay safe. Whether you’re a beginner or an experienced welder, knowing these details is important for your health and project success. Stay informed and protect yourself while working with this common material.

Credit: www.reddit.com
Introduction To Welding Galvanized Steel
Welding galvanized steel can be quite a challenge, but it is a skill worth mastering. Whether you’re a seasoned welder or just getting started, understanding how to handle this material is key. The process involves more than just striking an arc; it requires knowledge of the material’s properties, the right techniques, and some practical tips to get the best results.
Galvanized Steel Properties
Galvanized steel is simply steel that has been coated with a layer of zinc. This zinc coating protects the steel from rust and corrosion, making it an excellent choice for outdoor applications. However, this same coating can cause issues when welding. Why? Because zinc melts at a lower temperature than steel. When heated, it can release harmful fumes and create a porous weld.
Here’s a quick look at some of the key properties of galvanized steel:
- Corrosion Resistance: The zinc coating offers superb protection against rust.
- Durability: With proper care, galvanized steel structures can last for decades.
- Cost-Effective: It provides a long-lasting solution at a reasonable cost.
- Heat Sensitivity: The zinc layer can vaporize at welding temperatures, causing potential health risks.
Common Welding Methods
When it comes to welding galvanized steel, choosing the right method is crucial. Let’s explore some of the most common techniques:
- MIG Welding: This is a popular method because it is fast and produces a clean weld. However, it requires proper ventilation to deal with zinc fumes.
- TIG Welding: TIG welding offers precise control and high-quality welds, making it ideal for thin galvanized sheets. It’s slower but provides excellent results.
- Stick Welding: Also known as Shielded Metal Arc Welding (SMAW), this method is versatile and effective for thicker materials. It’s a bit messier but works well in various conditions.
Each method has its pros and cons, and the choice often depends on the specific project requirements. For instance, TIG welding might be the best option for delicate work, while MIG welding is great for speed.
| Welding Method | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
| MIG Welding | Fast, clean welds | Requires good ventilation |
| TIG Welding | Precise, high-quality welds | Slower, more skill required |
| Stick Welding | Versatile, good for thick materials | Messier, more spatter |
Choosing the right method can make all the difference. So, take your time to understand each technique and find what works best for your project. Remember, practice makes perfect!
Health Risks Of Welding Galvanized Steel
Welding galvanized steel can be a tricky business. It’s not just the spark and heat; there are some serious health risks you need to know about. When you weld this type of steel, dangerous fumes are released. These fumes can cause health issues if you’re not careful. Let’s dive into the details.
Inhalation Of Zinc Fumes
When you weld galvanized steel, the zinc coating on the metal can vaporize. This creates zinc fumes. Inhaling these fumes is not good for your health. You might not see these fumes, but they are there and can be harmful.
- Zinc Oxide: The main component of these fumes is zinc oxide. It forms when the zinc is heated.
- Invisible Threat: You can’t see the fumes, but they can still cause problems.
Short-term And Long-term Effects
Exposure to zinc fumes can have both immediate and lasting effects on your health. Let’s break it down:
Short-term Effects
In the short run, inhaling zinc fumes can cause something known as “metal fume fever.” Sounds scary, right? It is. Here are some symptoms:
- Fever: You might feel like you have the flu.
- Chills: Cold sweats and shivers are common.
- Nausea: Your stomach might feel upset.
- Headache: A pounding headache can occur.
- Fatigue: You could feel very tired.
Long-term Effects
What about the long haul? If you breathe in zinc fumes often, there could be more serious consequences:
- Lung Damage: Your lungs can get hurt over time.
- Respiratory Issues: Breathing can become harder.
It’s clear that welding galvanized steel comes with risks. But with the right precautions, you can protect yourself. Always work in a well-ventilated area, use the right safety gear, and don’t ignore the dangers. Stay safe out there!
Necessary Safety Equipment
Welding galvanized steel can be tricky and, let’s be honest, a bit dangerous. But hey, no need to panic. With the right safety equipment, you can protect yourself and get the job done smoothly. Let’s dive into the essential safety gear you need when welding galvanized steel.
Respiratory Protection
When you weld galvanized steel, it releases zinc oxide fumes. These fumes are not your friends. Breathing them in can cause metal fume fever, which feels like a bad flu. So, what’s the solution? A good quality respirator! Look for a respirator with a high-efficiency particulate air (HEPA) filter. It’s like having a personal bodyguard for your lungs.
- Choose a respirator rated for welding fumes.
- Ensure it fits snugly on your face.
- Replace filters regularly.
Remember, it’s not just about comfort—it’s about your health. Don’t skimp on this essential piece of gear.
Protective Clothing And Gear
Welding sparks and hot metal bits flying around can turn a fun project into a disaster if you’re not properly dressed. Think of protective clothing as your armor.
- Welding Helmet: Your eyes are precious. A helmet with a proper filter lens will protect you from harmful UV and infrared rays.
- Fire-Resistant Jacket: A good jacket will shield you from sparks and splatter.
- Welding Gloves: Keep your hands safe from burns with thick, heat-resistant gloves.
- Safety Boots: Steel-toe boots will protect your feet from heavy falling objects and hot metal.
Picture this: You’re in a full suit of protective gear, ready to conquer the welding world. Feels good, right? It’s not just about looking cool, though. This gear keeps you safe.
To sum up, welding galvanized steel is no walk in the park. But with the right safety equipment, you can weld confidently and stay safe. So, gear up, and happy welding!
Preparing The Workspace
Welding galvanized steel can be a tricky task. Preparing the workspace is crucial for safety and quality. By setting up correctly, you can avoid health risks and ensure a smooth process.
Ventilation Requirements
Ensure the workspace has good ventilation. Galvanized steel releases harmful fumes. Proper airflow is essential. Use exhaust fans or ventilation systems. Open doors and windows if possible. This helps disperse fumes quickly.
Workspace Organization
Keep the workspace tidy. Remove any clutter. A clean area reduces accidents. Organize your tools and materials. Keep them within reach. This improves efficiency and safety. Make sure you have a fire extinguisher nearby. Safety first.
Pre-welding Preparations
Welding galvanized steel is not as straightforward as it might seem. If you don’t prepare properly, you could face some serious issues. But don’t worry! With a bit of preparation, you can avoid these problems. In this section, we’ll look at what you need to do before you start welding galvanized steel. Let’s dive into the two main steps: Removing Galvanized Coating and Cleaning the Steel Surface.
Removing Galvanized Coating
One of the first things you need to do is remove the galvanized coating from the steel. Why? Because welding galvanized steel releases toxic fumes. These fumes can be harmful to your health. So, it’s crucial to get rid of the coating. Here’s how you can do it:
- Grinding: Use a grinder to remove the coating from the areas you plan to weld. Make sure to grind down to the bare steel.
- Chemical Stripping: You can also use a chemical stripper. This method is less labor-intensive but make sure to follow all safety guidelines.
- Sandblasting: If you have access to a sandblaster, this can be an effective way to remove the coating.
Remember, safety first! Always wear protective gear, including gloves, goggles, and a mask, when removing the coating.
Cleaning The Steel Surface
Once you’ve removed the galvanized coating, you need to clean the steel surface. A clean surface ensures a better weld. Here’s a simple guide:
- Degrease: Use a degreasing agent to remove any oil or grease. This step is important because contaminants can weaken your weld.
- Scrub: Use a wire brush to scrub the surface. This helps to remove any remaining dirt or rust.
- Rinse: Rinse the steel with clean water to wash away any debris or chemicals.
- Dry: Make sure the steel is completely dry before you start welding. Moisture can cause issues during the welding process.
Think of it like preparing a canvas for painting. You wouldn’t paint on a dirty surface, would you? The same principle applies here.
By taking these steps, you’ll set yourself up for successful welding. It might seem like extra work, but trust me, it’s worth it in the long run. After all, a well-prepared weld is a strong and safe weld. So, roll up your sleeves, and let’s get started!

Credit: www.youtube.com
Proper Welding Techniques
Welding galvanized steel can be tricky. If you don’t use the right techniques, the zinc coating can give you a hard time. It can cause problems like weak welds and toxic fumes. But don’t worry! With the right steps, you can get the job done safely and effectively. Here’s how:
Adjusting Welding Settings
First things first, let’s talk about your welding machine settings. Getting these right is crucial.
- Voltage: Lower the voltage to reduce spatter. Spatter can cause imperfections in your weld.
- Wire Feed Speed: A slower wire feed speed can help you control the weld pool better.
- Shielding Gas: Use a higher percentage of CO2 in your shielding gas. This helps break down the zinc coating faster.
Make these adjustments, and you’ll find it easier to work with galvanized steel. Think of it as tuning a guitar. If one string is off, the whole song sounds bad!
Controlling Heat Input
Now, let’s move on to heat input. Too much heat can cause the zinc to burn off too quickly, leading to weak welds.
- Shorter Welds: Make shorter welds to keep the heat down. This also helps in reducing the amount of zinc vapor.
- Pause and Cool: Take breaks between welds. This lets the material cool down and prevents overheating.
- Heat Sink: Use a heat sink, like a metal bar, to absorb some of the heat. This keeps the steel from getting too hot.
Controlling the heat is like cooking a steak. Too hot, and it’s burnt. Too cool, and it’s raw. You need just the right temperature!
By adjusting your welding settings and controlling heat input, you can weld galvanized steel like a pro. It’s all about balance and attention to detail. Happy welding!
Post-welding Procedures
Post-welding procedures are crucial after welding galvanized steel. These steps ensure the weld’s integrity and safety. Proper handling and inspection prevent future issues. Follow these procedures to maintain high-quality welds and safety standards.
Inspecting Weld Quality
Begin by checking the weld for any visible defects. Look for cracks, porosity, and incomplete fusion. Use a magnifying glass to inspect small details. Small issues can lead to bigger problems later. A thorough inspection helps catch these early.
Next, use non-destructive testing methods. Ultrasonic testing and dye penetrant tests are effective. These tests help find hidden flaws. They ensure the weld’s strength and durability. Always document your findings for future reference.
Handling Welded Pieces
Handle welded pieces with care to avoid damage. Use appropriate tools and safety gear. Protect your hands with gloves. Wear safety glasses to shield your eyes. Lift heavy pieces with the right equipment.
Store welded pieces in a clean, dry area. This prevents rust and contamination. Label the pieces clearly for easy identification. Keep a log of the storage conditions. This helps maintain the weld quality over time.
Environmental Considerations
Welding galvanized steel releases toxic fumes into the air. These fumes can harm both the environment and human health. Proper ventilation and protective gear are essential.
Welding galvanized steel has significant environmental implications. The coating on galvanized steel contains zinc. When welded, it releases hazardous fumes. These fumes can harm both the environment and human health. Proper precautions and responsible practices are essential.Disposal Of Waste Materials
Correct disposal of waste materials is crucial. Galvanized steel waste must be handled carefully. It may contain toxic substances. Proper disposal methods prevent soil and water contamination. Always follow local regulations for waste disposal. This ensures the environment stays safe.Reducing Environmental Impact
Reducing the environmental impact of welding galvanized steel involves several strategies. Use fume extraction systems. These systems capture harmful emissions. They keep the air clean. Choose eco-friendly welding materials. This helps reduce pollution. Train workers on best practices. Skilled workers minimize waste and errors. Such efforts protect the environment. “`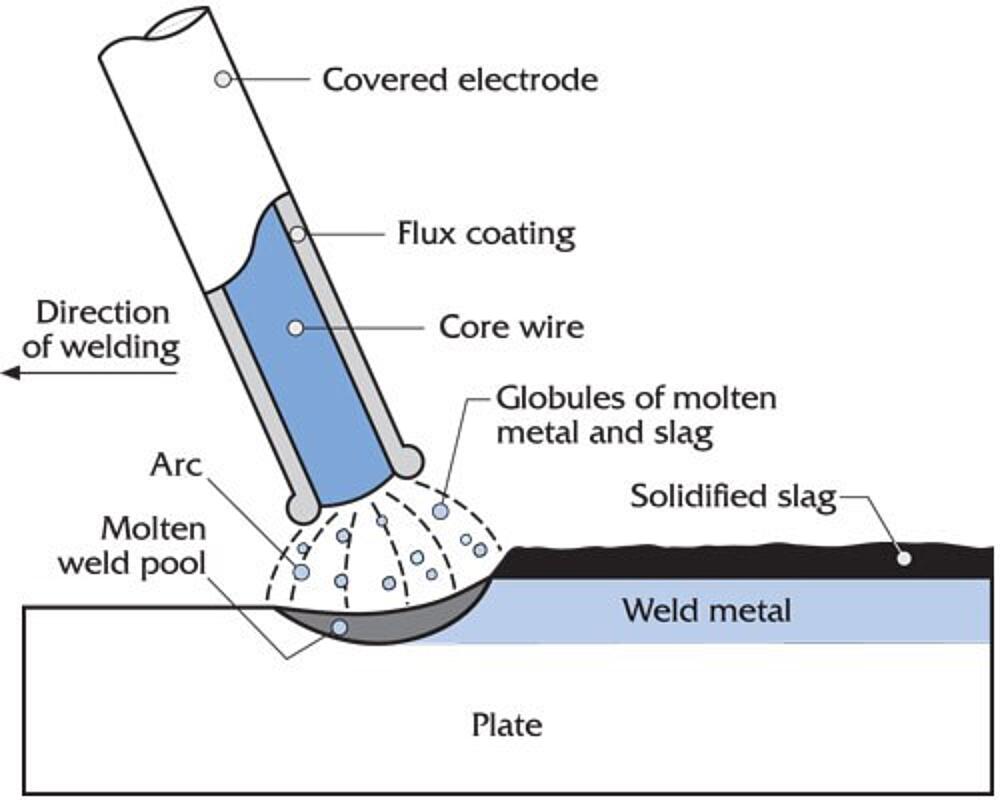
Credit: galvanizeit.org
Frequently Asked Questions
Why Do You Drink Milk After Welding Galvanized?
Drinking milk after welding galvanized metal may help reduce metal fume fever symptoms. Milk is believed to bind with zinc fumes, potentially alleviating irritation.
What Can Happen If You Weld Galvanized Steel?
Welding galvanized steel can release toxic zinc fumes. These fumes cause metal fume fever, which is harmful to health. Always weld in a well-ventilated area and wear proper protective gear.
Can Galvanized Steel Be Welded?
Yes, galvanized steel can be welded. Proper preparation, like removing the zinc coating, is essential. Use adequate ventilation to avoid harmful fumes.
Will Galvanized Steel Rust After Welding?
Yes, galvanized steel can rust after welding. The welding process can remove the protective zinc coating, exposing the steel to moisture and air. Applying a zinc-rich paint or re-galvanizing the welded area can help prevent rusting.
Conclusion
Welding galvanized steel requires caution and proper safety measures. Toxic fumes pose health risks. Adequate ventilation is crucial. Remove the zinc coating to reduce hazards. Wear protective gear always. Understand the material and prepare correctly. These steps ensure safety and quality results.
Welding can be safe with the right approach. Always prioritize safety in every project.

