Welding and soldering are two metal-joining techniques with distinct methods. Both processes serve different purposes in various industries.
Understanding the difference between welding and soldering is essential for choosing the right method. Welding involves melting the base metals to join them, creating a strong bond. Soldering, on the other hand, uses a filler metal that melts at a lower temperature than the base metals.
This method connects the metals without melting them. Each technique has its own applications, advantages, and limitations. Knowing these differences can help you decide which method to use for your specific needs. Whether you are a DIY enthusiast or a professional, understanding these processes will enhance your skills and projects. Let’s explore the key differences between welding and soldering.
Credit: www.youtube.com
Introduction To Welding And Soldering
Have you ever been curious about how metal pieces are joined together? If so, you might have come across the terms welding and soldering. While they may sound similar, they are actually quite different processes. In this blog post, we’ll explore the basics of welding and soldering, and see where each technique is commonly used. Let’s dive in!
Basic Definitions
Before we get into the details, let’s start with the definitions of each process:
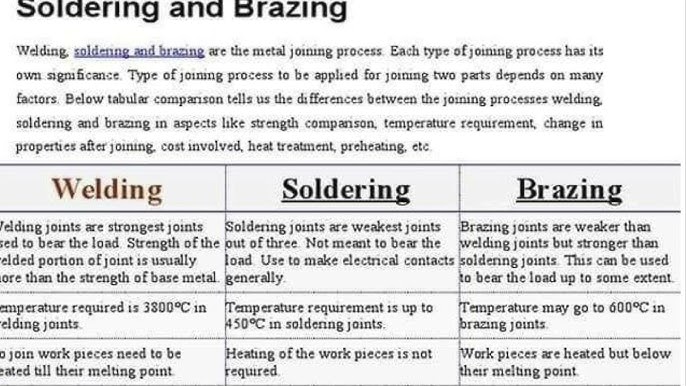
| Welding | Soldering |
|---|---|
| Welding is the process of joining two or more pieces of metal by melting them together. This creates a strong bond as the metals cool and solidify. | Soldering involves joining two or more metal pieces by melting a filler metal (solder) into the joint. The base metals do not melt; only the solder does. |
Common Applications
Welding and soldering are used in various industries and for different purposes. Here’s a quick look at some common applications:
- Welding:
- Construction: Building bridges, skyscrapers, and other structures.
- Automotive: Manufacturing and repairing cars and trucks.
- Shipbuilding: Constructing and repairing ships and submarines.
- Soldering:
- Electronics: Creating circuits and assembling components.
- Plumbing: Joining copper pipes for water systems.
- Jewelry: Making and repairing delicate metal pieces.
So, next time you see a towering skyscraper or use an electronic gadget, you might just appreciate the art and science behind welding and soldering a little more. These techniques may seem simple, but they are crucial in building and fixing many things we use every day. Happy metal joining!
Process Overview
Welding and soldering are two different techniques used to join materials. They both involve the application of heat but differ in process, materials used, and outcomes. Knowing the differences between welding and soldering is crucial for choosing the right method for your project.
How Welding Works
Welding involves melting the base metals to join them. A filler material is often added to form a strong joint. The process requires high heat, often exceeding 6,000 degrees Fahrenheit. This intense heat melts both the base metals and the filler material. As they cool, they solidify into a strong, durable bond. Common welding methods include MIG, TIG, and stick welding.
Welders use protective gear due to the high temperatures and bright light. The equipment includes a welding helmet, gloves, and sometimes a protective suit. Welding creates a permanent and robust joint, ideal for heavy-duty applications. Metals commonly welded include steel, aluminum, and stainless steel.
How Soldering Works
Soldering uses a lower temperature to join metals, usually below 840 degrees Fahrenheit. The process involves melting a filler metal, called solder, but not the base metals. The solder melts and flows into the joint, creating a bond as it cools. Soldering is often used for electrical connections and plumbing.
Soldering requires less protective gear. A soldering iron, flux, and solder wire are the primary tools. The soldering process is less intense and easier to control. It is suitable for delicate tasks, including electronic circuit boards. Metals commonly soldered include copper, brass, and sometimes silver.
Materials Used
Understanding the materials used in welding and soldering is crucial. These materials influence the strength and durability of the final product. Different materials also affect the process and quality of the joint. Let’s explore the specific materials used in welding and soldering.
Welding Materials
Welding often requires metals with high melting points. Common materials include steel, aluminum, and stainless steel. Welders frequently use filler materials like welding rods or wire. These fillers melt during the welding process, fusing the base metals together. The choice of filler material depends on the type of metal being welded.
Protective gases are also essential. Argon, helium, and carbon dioxide protect the weld area from contamination. These gases ensure a strong, clean weld. Different welding methods may require different gases. For example, MIG welding often uses argon or a mix of argon and carbon dioxide.
Soldering Materials
Soldering uses materials with lower melting points. Common base materials include copper, brass, and other metals used in electronics. The solder itself is a metal alloy, usually made of tin and lead. Lead-free solders are also available, often made of tin and silver or tin and copper.
Flux is another important material in soldering. It cleans the metal surfaces and helps the solder flow smoothly. Common types of flux include rosin-based flux for electronics and acid-based flux for plumbing. Choosing the right flux ensures a strong, reliable joint.
Equipment And Tools
When diving into the world of metalwork, understanding the difference between welding and soldering is crucial. The tools and equipment used in each process play a significant role. These tools determine the precision, strength, and type of joint you’ll achieve. Let’s break down the key differences in the equipment and tools used for welding and soldering.
Welding Tools
Welding involves joining metals by melting the base materials. This requires specialized tools that can generate high temperatures. Here are some common welding tools:
- Welding Machine: This is the heart of the operation. It generates the electrical current needed to create the weld. There are various types, including MIG, TIG, and Stick welders.
- Welding Helmet: Safety first! A welding helmet protects your face and eyes from the intense light and heat.
- Welding Rods: These are the filler materials that melt and bond the metal pieces together.
- Wire Feed: Used in MIG welding, this tool feeds wire automatically to maintain a steady flow.
- Clamps: Essential for holding metal pieces in place while you work.
Without these tools, welding would be nearly impossible. Each piece of equipment serves a unique purpose and ensures the strength and durability of the weld.
Soldering Tools
Soldering, on the other hand, involves joining metals at a much lower temperature. This process uses different tools and equipment:
- Soldering Iron: A handheld tool that heats up and melts the solder. It’s perfect for delicate tasks.
- Solder: The filler material, usually made of tin and lead, that melts and bonds the metals.
- Soldering Station: A base unit that controls the temperature of the soldering iron.
- Flux: A chemical cleaner that prevents oxidation and helps the solder flow smoothly.
- Desoldering Pump: Useful for removing solder if you need to redo a joint.
These tools ensure precision and control, making soldering ideal for electronics and small metal parts. The process is less about brute strength and more about careful application.
So, whether you’re welding a car frame or soldering a circuit board, having the right tools is essential. Each set of tools is tailored to the specific needs of the job, ensuring you get the best results every time.
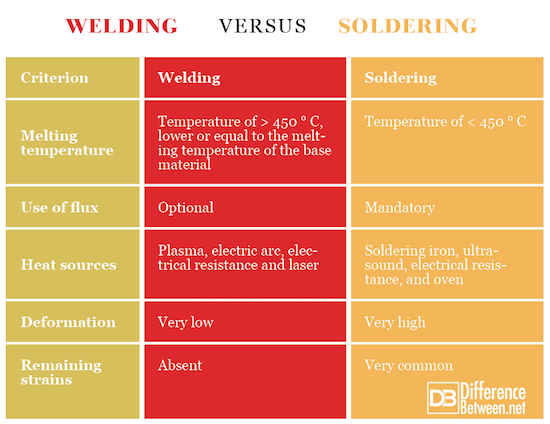
Temperature Differences
Understanding the temperature differences between welding and soldering is crucial. This knowledge can help you choose the right technique for your project. Let’s dive into the heat levels involved in both processes.
Heat Levels In Welding
Welding requires extremely high temperatures. Why? Because it melts the base metals to join them together. The heat can reach a staggering over 6,500 degrees Fahrenheit (around 3,600 degrees Celsius). Think of it as a miniature volcano in action!
- Arc Welding: Utilizes electric currents to produce the intense heat needed.
- Gas Welding: Employs a mixture of gases, often acetylene and oxygen, to achieve the high temperatures.
Ever tried frying an egg on a hot sidewalk? It’s a bit like that, only much, much hotter. The extreme heat ensures that the metals fuse strongly, creating a robust bond.
Heat Levels In Soldering
On the other hand, soldering is a much cooler affair. It typically uses temperatures below 850 degrees Fahrenheit (about 450 degrees Celsius). This is just hot enough to melt the solder but not the base metals.
- Soft Soldering: Uses temperatures around 400 degrees Fahrenheit (200 degrees Celsius), ideal for delicate electronics.
- Hard Soldering: Also known as brazing, requires higher temperatures, up to 850 degrees Fahrenheit (450 degrees Celsius), but still far below welding levels.
Imagine trying to toast a marshmallow without burning it—soldering is precise and controlled, perfect for intricate work. The lower temperatures mean that the base metals remain intact, while the solder flows smoothly to create a connection.
So, whether you’re welding or soldering, understanding the heat involved is key. It’s like choosing between a blowtorch and a gentle candle flame—each has its place, depending on the task at hand.
Credit: www.differencebetween.net
Strength And Durability
When it comes to joining metals, understanding the strength and durability of the joints is crucial. Whether you’re working on a DIY project or involved in professional manufacturing, knowing the difference between welding and soldering can help you choose the right method for your needs. Let’s explore how welded and soldered joints compare in terms of strength and durability.
Welded Joint Strength
Welding is a process that fuses two pieces of metal together by melting their edges. This results in a joint that is typically as strong as, or even stronger than, the original metal. Here’s why:
- Fusion: The metals are melted together, creating a strong bond.
- Filler Material: Sometimes, a filler material is added, which can enhance the joint’s strength.
- High Temperatures: The high temperatures involved ensure a deep and strong connection.
Imagine you’re building a metal frame for a heavy-duty project. You’d want something that can bear a lot of weight and withstand significant stress. Welding is your go-to method here. It creates a joint that can handle heavy loads and resist breaking under pressure. This is why welding is commonly used in construction, automotive, and aerospace industries.
Soldered Joint Strength
Soldering, on the other hand, involves joining metals using a filler metal with a lower melting point. This process doesn’t melt the base metals. Instead, it bonds them by melting the filler metal. Here’s what you need to know about soldered joints:
- Lower Temperatures: Soldering uses lower temperatures, which means less thermal stress on the components.
- Weaker Bond: The bond is not as strong as a welded joint because the base metals are not melted.
- Precision: It’s great for delicate tasks, like electronics, where precision is more important than strength.
Think of soldering like using glue for a craft project. It’s perfect for small, precise applications where you don’t need a super strong bond. Soldering is widely used in electronics, plumbing, and jewelry making. For instance, when fixing a circuit board, soldering provides the necessary connection without damaging the sensitive components.
In conclusion, the choice between welding and soldering depends on your project’s requirements. If you need a joint that can withstand significant stress and weight, welding is the way to go. For delicate, precise work, soldering is your best bet. Understanding these differences ensures you use the right technique for a durable and strong joint every time.
Safety Considerations
Understanding the difference between welding and soldering is crucial for safety. Both processes require careful handling and specific precautions. Let’s explore the safety considerations for each method.
Welding Safety
Welding involves high temperatures and intense light. Always wear a welding helmet with a face shield. This protects your eyes and face from sparks and UV light. Wear flame-resistant clothing to prevent burns. Thick gloves protect your hands from hot metal and sparks. Ensure proper ventilation to avoid inhaling harmful fumes. Keep a fire extinguisher nearby. The risk of fire is high with welding. Always work in a clean, clutter-free area.
Soldering Safety
Soldering uses lower temperatures but still poses risks. Wear safety glasses to protect your eyes from splashes. Use heat-resistant gloves to handle the soldering iron. Work in a well-ventilated area to avoid inhaling fumes. Always place the soldering iron in its stand when not in use. This prevents accidental burns. Never touch the tip of the soldering iron. It remains hot even after use. Keep your work area organized and free of flammable materials.
Typical Use Cases
Understanding the typical use cases of welding and soldering helps in choosing the right technique for a job. Each method has specific applications, making them essential in various industries. Let’s explore where welding and soldering shine.
Industrial Uses Of Welding
Welding plays a crucial role in construction and manufacturing. It fuses metals to build structures like bridges and buildings. Heavy machinery and vehicles also rely on welding. Think of cars, trains, and airplanes. Welding ensures strong, durable joints that can withstand heavy loads and stress.
Shipbuilding is another area where welding is indispensable. Large ships and submarines require precise and robust welding techniques. The oil and gas industry also depends on welding for pipelines and storage tanks. These structures need to handle high pressure and harsh environments.
Electronics And Soldering
Soldering is key in electronics manufacturing. It connects small components on circuit boards. Phones, computers, and TVs all use soldering. This method creates reliable electrical connections without melting the base materials.
Jewelry making also uses soldering. It joins precious metals without damaging them. This allows for detailed and intricate designs. Plumbing often employs soldering to connect copper pipes. It creates leak-proof seals that ensure water flows smoothly.
In summary, welding is best for heavy-duty tasks. Soldering excels in precision work. Each technique has its unique place in various industries.
Pros And Cons
Whether you’re fixing a broken gate or creating delicate electronics, choosing the right method is crucial. Welding and soldering are two popular techniques, but each has its own advantages and disadvantages. Let’s dive into the pros and cons of welding and soldering to help you decide which method is best for your project.
Advantages Of Welding
Welding is known for its strength and durability. Here are some key benefits:
- Strong Joints: Welded joints are very strong and can handle heavy loads.
- Permanence: Welding creates permanent bonds that last for a long time.
- Diverse Applications: You can use welding for a variety of materials, including steel and aluminum.
- High Temperature Resistance: Welded joints can withstand high temperatures, making them ideal for industrial use.
However, welding does have its downsides. For instance, it requires specialized equipment and training. This can make it more expensive and less accessible to beginners.
Advantages Of Soldering
On the flip side, soldering offers its own set of benefits, especially for smaller or more delicate tasks:
- Low Temperature: Soldering uses lower temperatures, which means less risk of damaging sensitive components.
- Precision: It allows for precise work, making it perfect for electronics and small repairs.
- Accessibility: Soldering is generally easier to learn and requires less expensive equipment.
- Reworkable: If you make a mistake, you can easily rework soldered joints without much hassle.
But, like welding, soldering has its limitations. Soldered joints are not as strong and can’t handle high-stress applications. They are also less durable in high-temperature environments.
In conclusion, whether you choose welding or soldering depends on your specific needs. If you need strong, durable joints and can invest in the proper equipment, welding is the way to go. On the other hand, for precise, smaller tasks, soldering is often the better choice. Happy joining!
Credit: blog.red-d-arc.com
Frequently Asked Questions
Is Soldering As Strong As Welding?
Soldering is not as strong as welding. Welding creates a stronger bond by melting and fusing base metals. Soldering joins metals using a filler material without melting the base metals. Welding is typically used for structural applications, while soldering is suited for electronics and delicate tasks.
What Is The Difference Between Soldering And Welding?
Soldering uses a filler metal with a low melting point to join materials. Welding fuses materials together at high temperatures.
What Are The Advantages Of Soldering Over Welding?
Soldering uses lower temperatures, reducing the risk of warping materials. It’s ideal for delicate components and creates cleaner joints. Soldering requires less equipment and is generally faster and more cost-effective than welding.
Can Solder Act As Weld?
No, solder cannot act as weld. Soldering involves melting a filler metal to join parts, while welding fuses the materials together.
Conclusion
Welding and soldering are distinct techniques with different applications. Welding joins metals by melting them together. Soldering connects pieces using a filler metal without melting the base metals. Welding is stronger, suitable for heavy-duty tasks. Soldering is ideal for delicate work, like electronics.
Both techniques have their unique benefits. Choosing the right method depends on your project’s needs. Understanding these differences helps you make informed decisions. Whether you need strong bonds or precision, knowing these techniques is essential.

