Welding and soldering are both techniques used to join materials. But they are quite different.
Welding is used to fuse metals by melting them. Soldering, on the other hand, uses a filler metal to join materials without melting the base materials. Understanding the differences between welding and soldering is crucial. These methods serve different purposes and require different skills.
Welding is common in construction and manufacturing, creating strong, permanent joints. Soldering is often used in electronics and plumbing, where precise, less-strong joints are needed. Knowing which technique to use can save time, money, and effort. This guide will help clarify the differences, making it easier to choose the right method for your project. Let’s dive into the specific contrasts between welding and soldering.
Introduction To Welding And Soldering
Welding and soldering are two techniques often used in metalwork and electronics. Despite both involving the joining of materials, they are quite different. Understanding these differences is important whether you’re a hobbyist or a professional. Let’s dive into what sets these two methods apart.
Definition Of Welding
Welding is the process of joining two pieces of metal together by melting them at high temperatures. Here, the base metals melt and fuse together to form a strong bond. Typically, a filler material is also used to enhance the bond. This method is often employed in construction, automotive repair, and manufacturing.
Welding can be categorized into different types:
- Arc Welding: Uses an electric arc to melt metals.
- MIG Welding: Uses a wire feeding gun that feeds wire at an adjustable speed and uses a constant voltage.
- TIG Welding: Uses a tungsten electrode to produce the weld.
Welding requires a high degree of skill and safety precautions, like wearing protective gear to prevent burns and eye damage.
Definition Of Soldering
Soldering is the process of joining two or more metal items by melting and flowing a filler metal (solder) into the joint. Unlike welding, the base metals do not melt. The solder has a lower melting point than the base metals, which makes this process suitable for delicate electronics and plumbing.
Here are some common soldering types:
- Soft Soldering: Uses a solder with a low melting point, ideal for electronics.
- Hard Soldering: Uses a solder with a higher melting point, often for jewelry and piping.
- Silver Soldering: A type of hard soldering that uses silver as the filler material.
Soldering is generally easier to learn than welding and requires less specialized equipment. However, it still requires precision and practice to master.
Credit: www.electronicshub.org
Materials Used
Understanding the materials used in welding and soldering is important. Different processes need specific materials. This section highlights the key materials used in both welding and soldering.
Metals In Welding
Welding usually involves metals like steel, aluminum, and stainless steel. These metals are strong and can withstand high temperatures. Welders often use these metals in construction and manufacturing. Steel is common because it is durable and versatile. Stainless steel is resistant to rust, making it ideal for many projects. Aluminum is lightweight and used in aerospace and automotive industries.
Alloys In Soldering
Soldering primarily uses alloys, a mix of metals. Common alloys include tin-lead, tin-silver, and tin-copper. Tin-lead alloy is popular in electronics for its low melting point. Tin-silver alloy is lead-free and used in plumbing and electronics. Tin-copper alloy is also lead-free and common in electronics and jewelry. These alloys melt easily and create strong bonds at low temperatures.
Temperature Requirements
Understanding the temperature requirements for welding and soldering is key. These processes involve joining materials, but they differ significantly in the heat needed. Let’s explore the temperature differences between welding and soldering.
High Temperatures In Welding
Welding requires very high temperatures to melt materials. The temperatures often exceed 2,500 degrees Fahrenheit. This intense heat fuses metals together, creating a strong bond. Various welding techniques may require different temperature ranges. For instance, arc welding uses an electric arc to generate heat. Gas welding, on the other hand, uses a gas flame. Both methods reach high temperatures to melt the base metals.
Low Temperatures In Soldering
Soldering operates at much lower temperatures compared to welding. Typically, soldering uses heat below 800 degrees Fahrenheit. This process does not melt the base metals. Instead, it melts a filler metal called solder. This solder has a lower melting point, around 400 degrees Fahrenheit. This makes soldering ideal for delicate tasks. It joins electronic components without damaging them.
Strength Of Joints
When it comes to joining metals, the strength of the joint is a key factor. Whether you’re fixing a broken pipe or assembling intricate electronics, you need to know how strong the connection will be. In this post, we’ll dive into the strength of joints in welding and soldering. Let’s find out which method holds up better under pressure!
Welded Joints
Welded joints are known for their incredible strength. When you weld two pieces of metal together, you’re essentially fusing them into one solid piece. This process involves melting the metals at very high temperatures and then allowing them to cool and solidify. The result? A joint that is as strong as the parent metal itself.
Welded joints are commonly used in construction, automotive industries, and even in making spacecraft. Why? Because they can withstand heavy loads and extreme conditions. Imagine a skyscraper or a bridge – these structures rely on the robustness of welded joints to stay intact.
Here’s a quick look at the strengths of welded joints:
- High Load Capacity: Can handle heavy weights and pressures.
- Durability: Lasts long without deteriorating.
- Seamless Connection: The joint is almost as strong as the metal itself.
Soldered Joints
Soldered joints, on the other hand, are a bit different. Soldering involves melting a filler metal (called solder) to join two metal pieces without melting the base metals. This technique is commonly used in electronics, plumbing, and jewelry making.
While soldered joints may not be as strong as welded ones, they have their own unique advantages. They are perfect for delicate tasks where high temperatures could damage the components. For example, in circuit boards, soldering ensures a stable connection without harming the tiny parts.
Let’s break down the strengths of soldered joints:
- Precision: Ideal for small, detailed work.
- Low-Temperature Process: Reduces the risk of damaging sensitive components.
- Flexibility: Easy to rework or repair if needed.
So, whether you’re building a towering structure or assembling a circuit board, the choice between welding and soldering depends on the strength you need. Both methods have their place in the world of metalwork, each offering unique benefits.
Applications And Uses
Welding and soldering might seem similar, but they serve distinct purposes in various fields. While both are techniques used to join materials, their applications and uses are quite different. Let’s dive into where each technique is commonly utilized.
Industrial Uses Of Welding
Welding is a powerhouse in the industrial sector. It’s used to construct everything from skyscrapers to ships. Think about the last time you saw a massive bridge or a towering building – chances are, welding played a critical role in putting those metal structures together.
- Construction: Welding is essential in building infrastructure like bridges, buildings, and highways.
- Automotive: Car frames, engines, and exhaust systems are welded for strength and durability.
- Aerospace: Airplanes and spacecraft rely on precise welding to ensure safety and performance.
- Shipbuilding: Ships and submarines require robust welding to withstand the harsh marine environment.
Here’s a fun fact: the Eiffel Tower, a global icon, was constructed using iron welding. Imagine the skill and precision needed for such a monumental task!
Common Uses Of Soldering
Soldering, on the other hand, is often associated with electronics and delicate work. Unlike welding, soldering involves lower temperatures and is ideal for joining small components without damaging them.
- Electronics: Soldering is crucial in creating and repairing circuit boards and electronic devices.
- Plumbing: It is used to join copper pipes in plumbing systems.
- Jewelry Making: Jewelers use soldering to create intricate designs and fix broken pieces.
- Crafts: Hobbyists and artists often use soldering for small metal projects and crafts.
Picture this: you’re fixing a broken radio. The delicate components inside would be a nightmare to repair with welding. That’s where soldering shines, providing precision without the heat damage.
In summary, while welding and soldering might appear similar, their applications couldn’t be more different. Welding is the go-to for heavy-duty industrial projects, while soldering is perfect for fine, detailed work. Understanding these differences helps in choosing the right technique for your project, ensuring strength and precision where needed.
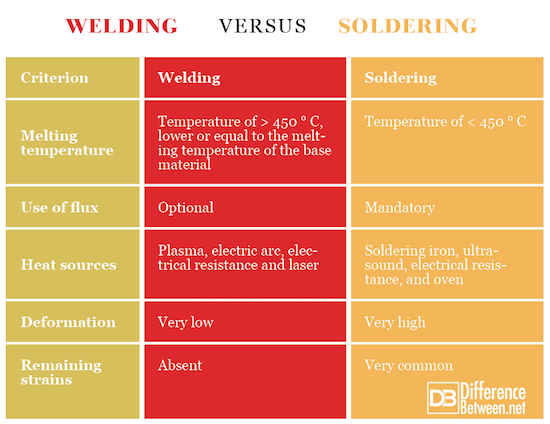
Credit: www.differencebetween.net
Equipment And Tools
Understanding the equipment and tools used in welding and soldering is crucial. Each technique requires specific instruments to perform the tasks effectively. This section highlights the key equipment and tools used in both welding and soldering.
Welding Equipment
Welding involves joining metals through high heat. The main tool is a welding machine. It generates the heat needed to melt the metals. There are various types of welding machines. The common ones include MIG, TIG, and Stick welders.
MIG welders use a wire electrode to create the weld. TIG welders use a tungsten electrode. Stick welders use a consumable electrode. Each has its own advantages. The choice depends on the project requirements.
Other essential tools include welding rods, clamps, and a chipping hammer. Welders also use protective gear. Helmets, gloves, and aprons are crucial for safety. Without them, welders risk severe injuries.
Soldering Tools
Soldering is a technique for joining metals with a filler metal. The main tool is a soldering iron. It heats the filler metal, known as solder. Solder melts at a low temperature, usually below 840°F. This makes soldering different from welding.
Soldering irons come in various types. There are electric, gas-powered, and battery-operated models. Each type has specific uses. Electric soldering irons are common for electronics. Gas-powered irons are useful for fieldwork.
Additional tools include solder wire, flux, and a soldering stand. Solder wire is usually made of tin and lead. Flux helps clean the metal surfaces. A soldering stand holds the hot iron safely. Safety glasses and ventilation are also important for protection.
Safety Considerations
When it comes to welding and soldering, safety is key. Both processes involve heat and can pose risks if not handled properly. Whether you are a beginner or a seasoned pro, understanding the safety considerations is crucial. Let’s dive into the safety aspects of welding and soldering to ensure you can work confidently and safely.
Welding Safety
Welding is a powerful process that joins materials together. However, it can be dangerous if safety protocols are not followed. Here are some key points to keep in mind:
- Protective Gear: Always wear a welding helmet, gloves, and protective clothing. These will shield you from sparks, heat, and harmful radiation.
- Ventilation: Welding produces fumes. Ensure your workspace is well-ventilated to avoid inhaling toxic gases.
- Fire Hazards: Keep a fire extinguisher nearby. Welding involves high temperatures and can easily ignite flammable materials.
- Electrical Safety: Welding equipment uses high voltage. Ensure all cables are in good condition and avoid working in damp areas.
Remember, safety first. It’s better to spend a few minutes on precautions than deal with an accident later.
Soldering Safety
Soldering might seem less intense compared to welding, but it still requires attention to safety. Here’s what you need to know:
- Eye Protection: Wear safety glasses to protect your eyes from solder splashes.
- Work Area: Keep your workspace clean. Soldering involves small components, and a clutter-free area will prevent accidents.
- Heat Burns: The soldering iron gets extremely hot. Handle it with care and always place it on a stand when not in use.
- Fume Extraction: Soldering produces fumes. Use a fume extractor or work in a well-ventilated area to avoid inhaling harmful particles.
Even though soldering is less intense, don’t let your guard down. Safety practices are essential to avoid injuries and health issues.
In conclusion, both welding and soldering come with their own set of safety considerations. Whether you are fusing metal parts or joining tiny electronic components, always prioritize safety. With the right precautions, you can enjoy your work without unnecessary risks. Stay safe and happy crafting!
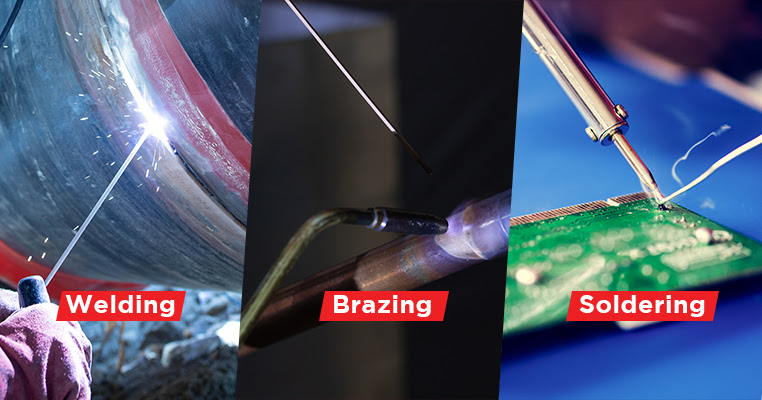
Credit: blog.red-d-arc.com
Skill And Training Requirements
Understanding the skill and training requirements for welding and soldering is crucial. Both processes involve joining materials but differ significantly in technique and expertise. Let’s explore the specific skills needed for each practice.
Welding Skills
Welding requires a high level of precision and dexterity. Welders need to understand different metals and their properties. They must master various welding techniques like MIG, TIG, and Stick welding. Safety is a crucial aspect, requiring knowledge of protective gear and safe practices. Welders often undergo formal training programs and apprenticeships. This ensures they are well-versed in the tools and techniques required. Certification may also be necessary for specific industries.
Soldering Skills
Soldering involves joining small electronic components. This requires a steady hand and attention to detail. Soldering skills are often learned through practice and basic training. Understanding the properties of solder and flux is essential. Solderers must know how to handle a soldering iron safely. Precision is key in avoiding damage to delicate components. Training programs for soldering are generally shorter and less intensive than welding.
Cost Implications
Understanding the cost implications is essential when choosing between welding and soldering. Both processes have distinct cost factors that impact budgeting. Let’s dive into the specifics of each.
Cost Of Welding
Welding generally involves higher costs. The equipment required for welding is often expensive. Advanced welding machines and safety gear add to the cost. Additionally, welding uses more power, which increases electricity bills. The materials used in welding, like filler metals, also contribute to the expense. Skilled labor for welding is usually pricier due to the expertise needed.
Cost Of Soldering
Soldering tends to be more affordable. The equipment for soldering is less expensive. Simple soldering irons and basic safety gear are all that’s needed. Soldering uses less power, resulting in lower electricity costs. The materials, such as solder and flux, are cheaper than welding materials. Skilled labor for soldering is also less expensive. The process is simpler, requiring less specialized training.
Environmental Impact
Welding and soldering impact the environment differently. Welding uses higher temperatures and produces more fumes. Soldering, with lower temperatures, emits fewer harmful gases.
Understanding the environmental impact of welding and soldering is crucial. Both processes affect the environment differently. This section will explore these differences.Welding Impact
Welding uses high energy to join metals. This process produces fumes and gases. These emissions can harm the environment. Welding often requires electricity or fuel. Both sources contribute to pollution. Additionally, welding generates heat. Excessive heat can damage the surroundings. The waste materials from welding can also be harmful. They include metal scraps and chemical residues.Soldering Impact
Soldering uses lower temperatures than welding. This means it produces fewer harmful gases. The environmental impact is generally less severe. Soldering uses solder, a metal alloy. Some solder materials contain lead. Lead is toxic and can contaminate soil and water. Newer solders are lead-free. But they still have environmental concerns. The flux used in soldering can also be harmful. It can release toxic fumes if not handled properly. “`Frequently Asked Questions
How Is Soldering Different From Welding?
Soldering joins metals using a filler metal with a lower melting point than the workpieces. Welding fuses metals directly using high heat. Soldering is for delicate tasks, while welding handles structural work.
What Is The Difference Between Welding And Soldering Lead?
Welding involves melting and fusing materials, typically metals, using high heat. Soldering joins metals using a filler metal, like lead, at lower temperatures. Welding creates stronger bonds than soldering.
Can Soldering Be Used To Weld?
No, soldering cannot be used to weld. Soldering joins metals using a filler metal with a lower melting point. Welding fuses metals by melting them together.
What Are The Advantages Of Soldering Over Welding?
Soldering requires lower temperatures, reducing the risk of damaging components. It’s ideal for delicate electronics and provides a cleaner finish. Soldering is also faster, cost-effective, and easier for beginners compared to welding.
Conclusion
Welding and soldering serve different purposes in metalwork. Welding joins metals by melting them. Soldering connects metals using a filler. Welding is stronger, suited for heavy-duty tasks. Soldering is ideal for delicate electronics. Each technique has its own tools and skills.
Choose welding for structural projects. Opt for soldering in electronic repairs. Understanding their differences helps in selecting the right method. Always consider the material and project requirements. Proper technique ensures a strong, lasting bond. Now you can decide which method fits your needs best.

