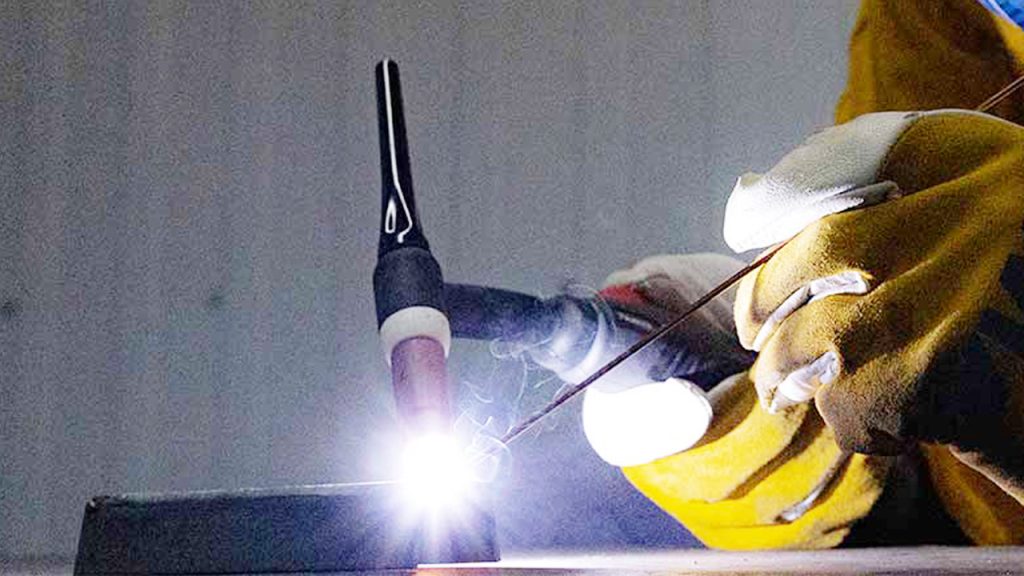
A welding machine joins metal parts together using heat and pressure. It produces a strong, durable bond by melting the metal at the joint.
Understanding how a welding machine works is crucial for anyone interested in metalwork. These machines come in various types, each suited for specific tasks. They use electricity to create heat, which melts the metal. Then, as the metal cools, it solidifies to form a strong bond.
Knowing the basics can help you choose the right machine and use it safely. This knowledge is essential whether you’re a hobbyist or a professional. Let’s explore the fascinating world of welding machines and how they operate.

Credit: www.nu-tech.us
Introduction To Welding Machines
Welding machines are fascinating tools used in a wide range of industries. From construction sites to artistic metalwork, these devices play a crucial role in creating strong, durable bonds between materials. But how exactly do these machines work? In this blog post, we’ll dive into the basics of welding machines, breaking down the process in simple terms that anyone can understand. Whether you’re a beginner or just curious about welding, this guide will provide you with a clear understanding of how these powerful machines operate.
What Is Welding?
Welding is a process that joins two materials, usually metals or thermoplastics, by applying heat, pressure, or both. The heat melts the materials at the joining point, allowing them to fuse together as they cool and solidify. Think of it as a super-strong glue, but instead of using adhesive, we use intense heat to bond the materials.
Welding is essential in many industries because it creates strong, permanent connections that can withstand high stress and pressure. From building skyscrapers to repairing cars, welding is an indispensable skill. And the tool that makes all of this possible? The welding machine.
Types Of Welding Machines
There are several types of welding machines, each designed for specific applications and welding techniques. Here are the most common types:
- MIG Welders (Metal Inert Gas): These machines use a wire electrode that is fed through a welding gun. The arc is created between the electrode and the metal, melting both to form a weld. MIG welding is popular for its speed and ease of use, making it ideal for beginners.
- TIG Welders (Tungsten Inert Gas): TIG welding uses a non-consumable tungsten electrode to produce the weld. A separate filler material is often used. This method provides precise control and is excellent for welding thin materials and intricate designs.
- Stick Welders (Shielded Metal Arc Welding): Stick welding uses a consumable electrode coated in flux. The arc is struck between the electrode and the metal, melting both to form the weld. This method is versatile and effective for welding thicker materials.
Each type of welding machine has its strengths and is suitable for different tasks. For instance, if you’re working on a large construction project, a MIG welder might be your go-to tool. On the other hand, if you’re creating delicate metal sculptures, a TIG welder could be the better choice.
So, there you have it! A basic introduction to welding machines. Next time you see a welder at work, you’ll have a better understanding of the incredible process happening right before your eyes. Stay tuned for more detailed guides and tips on how to master the art of welding!
Components Of A Welding Machine
Welding machines are complex tools with several key components. These components work together to create strong and durable welds. Understanding each part can help you use the machine better and ensure safety.
Power Source
The power source is the heart of the welding machine. It provides the necessary electrical energy to generate heat. Different welding machines use various types of power sources. Some use AC (alternating current), while others use DC (direct current). The choice depends on the welding process and the materials used.
Electrode
The electrode is a crucial part of the welding process. It conducts the current from the power source to the workpiece. There are different types of electrodes. Some are consumable, while others are non-consumable. Consumable electrodes melt and become part of the weld. Non-consumable electrodes do not melt and are used mainly in TIG welding.
Welding Torch
The welding torch is the tool that directs the electrode to the workpiece. It also provides shielding gas in some welding processes. The torch must be handled carefully to ensure a stable arc and quality weld. Different torches are designed for various welding methods. Choose the right one for your specific task.
How Welding Machines Generate Heat
Welding machines are fascinating tools that join metals together by generating intense heat. This heat is crucial as it melts the metal edges, allowing them to fuse seamlessly. But how exactly do these machines generate such high temperatures? Let’s delve into the mechanics behind the heat generation in welding machines.
Electric Arc
One common method of generating heat in welding machines is through an electric arc. This process involves creating a continuous electrical discharge between an electrode and the metal workpiece. Imagine striking a match – the spark that results is akin to the electric arc in welding. This arc generates extreme heat, often reaching temperatures over 6,000 degrees Fahrenheit.
Here’s how it works in simple terms:
- The welding machine feeds electrical current to the electrode.
- When the electrode is close to the metal, an arc forms.
- The arc’s heat melts the metal, allowing for fusion.
This technique is widely used in various types of welding, including stick welding and MIG welding. It’s efficient, powerful, and effective in melting even the toughest metals.
Resistance Heating
Another intriguing method is resistance heating. This method leverages the resistance of the metal to the flow of electrical current. Think of it like rubbing your hands together on a cold day – the friction generates heat. In resistance welding, the metal’s resistance to electrical current produces the necessary heat.
Here’s the process broken down:
- Electrical current passes through the metal pieces to be welded.
- The resistance of the metal to the current flow generates heat.
- The heat produced melts the metal at the joint, forming a strong bond.
Resistance heating is commonly used in spot welding and seam welding. It’s quick, efficient, and ideal for welding thin sheets of metal.
Both these methods – electric arc and resistance heating – are integral in the world of welding. They enable welders to create strong, durable joints in various materials. Next time you see a welded structure, you’ll know a bit more about the heat magic behind it!

Credit: www.youtube.com
Welding Processes Explained
Welding is a fascinating skill. It’s like magic—turning metal into art or building structures that last a lifetime. But how does it really work? Let’s dive into the world of welding processes. We’ll explore the different types of welding: MIG, TIG, and Stick. Each has its own charm and specific uses. So, sit tight and let’s unravel these techniques together.
Mig Welding
MIG stands for Metal Inert Gas. It’s also known as Gas Metal Arc Welding (GMAW). This process is quite popular because it’s easy to learn and use. Imagine you are painting with a spray can, but instead of paint, you’re using a wire to weld metal.
- How it works: A wire is fed through the welding gun. An electric arc forms between the wire and the metal, melting both. The melted metal then joins together.
- Shielding Gas: This process uses a shielding gas to protect the weld from contaminants in the air. Common gases include argon and carbon dioxide.
Fun Fact: MIG welding is often used in automotive repairs, making it a favorite among car enthusiasts!
Tig Welding
TIG stands for Tungsten Inert Gas, also known as Gas Tungsten Arc Welding (GTAW). This method is a bit more complex, but it produces very clean and precise welds. Think of TIG welding as the fine brush used by an artist to create detailed work.
- How it works: A non-consumable tungsten electrode creates the weld. The heat from the arc melts the metal. You can add filler metal if needed.
- Shielding Gas: Argon or helium gas is used to protect the weld from oxidation.
Did You Know? TIG welding is often used in aerospace and automotive industries because of its precision and strength.
Stick Welding
Stick welding, or Shielded Metal Arc Welding (SMAW), is the granddad of welding techniques. It’s been around for ages and is known for its simplicity and versatility. Imagine you’re drawing with a crayon, but this crayon is made of metal.
- How it works: An electrode, or “stick,” is used to create the weld. The electric arc melts the electrode and the metal. The melted electrode acts as filler metal.
- Shielding: The electrode is coated with flux, which creates a protective gas shield when it burns. This shield keeps the weld safe from impurities.
Interesting Tidbit: Stick welding is perfect for outdoor work and on rusty or dirty metals, making it a favorite for construction and repair jobs.
So, there you have it! The basics of MIG, TIG, and Stick welding. Each process has its own unique features and applications. Whether you’re fixing a car, building a plane, or putting up a fence, there’s a welding technique just right for the job. Happy welding!
Safety Measures
Welding involves intense heat and bright light. It can be dangerous. Therefore, following safety measures is crucial. Protecting yourself and others is a top priority in welding.
Personal Protective Equipment
Always wear a welding helmet. It shields your eyes from harmful light. Use gloves to protect your hands from burns. Wear a long-sleeved shirt and pants. They safeguard your skin from sparks and heat.
Boots are essential. They protect your feet from falling objects. Respirators are also important. They help you avoid inhaling harmful fumes. Ear protection is necessary in noisy environments.
Workplace Safety
Keep your workspace clean. Remove flammable materials. Ensure proper ventilation to avoid fumes. Always check your equipment before use. Make sure all connections are secure.
Have a fire extinguisher nearby. It is vital for emergencies. Mark hazardous areas clearly. Everyone should know the safety rules. Training is essential for all workers.
Common Welding Techniques
Welding is a vital process in manufacturing, construction, and repair. Understanding common welding techniques helps in selecting the right method for the job. Let’s explore some of the most widely used welding joints.
Butt Joints
Butt joints are the simplest type of welding joint. Two metal pieces are placed edge to edge. This technique is ideal for joining two flat pieces together. It is commonly used in pipelines and structural steel fabrication. The process requires precise alignment for a strong weld.
Lap Joints
Lap joints involve overlapping two metal pieces. The weld is applied along the edges where the pieces overlap. This method is commonly used for sheet metal. It offers good strength and is easy to perform. Lap joints are useful for materials of different thicknesses.
T-joints
T-joints form a “T” shape by welding one piece perpendicular to another. This technique is often used in the construction of frames and supports. The weld is applied at the intersection of the two pieces. T-joints require proper angle and fit for a strong connection.
Maintenance Of Welding Machines
Maintaining your welding machine is crucial. It keeps the machine in top shape, ensures safety, and extends its lifespan. But how do you maintain it? Here, we break down the steps into simple parts: routine checks and troubleshooting. Let’s dive in!
Routine Checks
Regular maintenance is like a health check-up for your welding machine. These routine checks can prevent bigger problems down the line.
- Inspect the Cables: Look for any cuts or wear and tear on the cables. Damaged cables can be dangerous and affect the welding quality.
- Clean the Machine: Dust and dirt can clog the machine. Use a soft cloth to wipe it down. A clean machine works better and lasts longer.
- Check the Connections: Ensure all connections are tight. Loose connections can cause poor performance or even accidents.
- Examine the Electrode Holder: Make sure the holder is clean and not worn out. A good holder ensures a stable arc.
Troubleshooting
Even with the best maintenance, things can go wrong. Here’s how you can troubleshoot common issues.
- Machine Won’t Turn On: Check the power supply first. Is it plugged in? Is the switch on? If yes, check the fuse. A blown fuse can be the culprit.
- Poor Weld Quality: This can happen due to various reasons. Check the electrode and wire feed. They might need adjustment. Also, ensure the metal surface is clean.
- Overheating: If your machine gets too hot, it may shut down automatically. Ensure it’s in a well-ventilated area. Let it cool down before using it again.
- Sparking Issues: If the machine sparks too much, check the grounding. Proper grounding can solve this problem.
Remember, regular maintenance is key to keeping your welding machine in top shape. Taking a few minutes to check and clean can save you from headaches down the road. Plus, it ensures your safety and produces better welds. So, make it a habit!
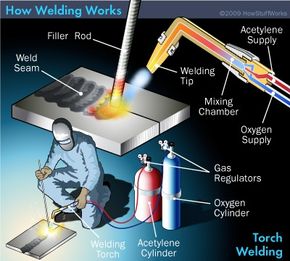
Credit: science.howstuffworks.com
Applications Of Welding
Welding is essential in various industries. Its applications range from construction to automotive manufacturing. Understanding these applications can highlight the importance of welding in everyday life. Let’s explore some key industries where welding plays a crucial role.
Construction
Welding is a cornerstone in the construction industry. It is used to build structures like bridges, buildings, and pipelines. Welders join steel beams and other metal parts to ensure stability. This creates strong and long-lasting structures. Welding also helps in repair work for damaged structures. This makes construction projects safer and more reliable.
Manufacturing
Manufacturing relies heavily on welding for production. Factories use welding to create machinery, tools, and appliances. It is crucial in the assembly of various products. From small electronic devices to large industrial machines. Welding ensures products are durable and functional. This helps manufacturers meet high-quality standards. It also plays a role in maintaining and repairing factory equipment. This minimizes downtime and increases efficiency.
Automotive Industry
The automotive industry depends on welding for vehicle production. Welding joins car parts like the chassis, body panels, and exhaust systems. This ensures vehicles are strong and safe. Welding also helps in the repair and customization of vehicles. This allows for modifications and upgrades. Welders work in car factories, repair shops, and custom car workshops. Their skills are essential for producing and maintaining quality vehicles.
Frequently Asked Questions
How Does A Welding Machine Work?
A welding machine generates heat to melt and fuse materials, usually metals, by creating an electric arc. The process joins materials together, forming a strong bond.
How Does Welding Work Step By Step?
Welding joins metals by melting them together. The process involves heating metal parts. A filler material may be added. The molten metals cool and solidify, forming a strong joint. Various welding methods exist, such as MIG, TIG, and stick welding.
Proper safety gear is essential.
Why Doesn’t The Welding Machine Shock You?
Welding machines use low voltage, which reduces the risk of shock. Proper insulation and safety measures also protect users.
What Is Inside A Welding Machine?
A welding machine contains a transformer, rectifier, control circuit, cooling fan, and power supply. These components generate and control the welding arc.
Conclusion
Welding machines play a crucial role in metalwork. They join metal pieces by melting them. This process creates strong, lasting bonds. Understanding how welding machines work helps in choosing the right one. Remember, safety comes first in any welding task.
Use proper gear and follow guidelines. With practice, your welding skills will improve. Stay curious and keep learning. Your projects will benefit greatly from this knowledge. Happy welding!

