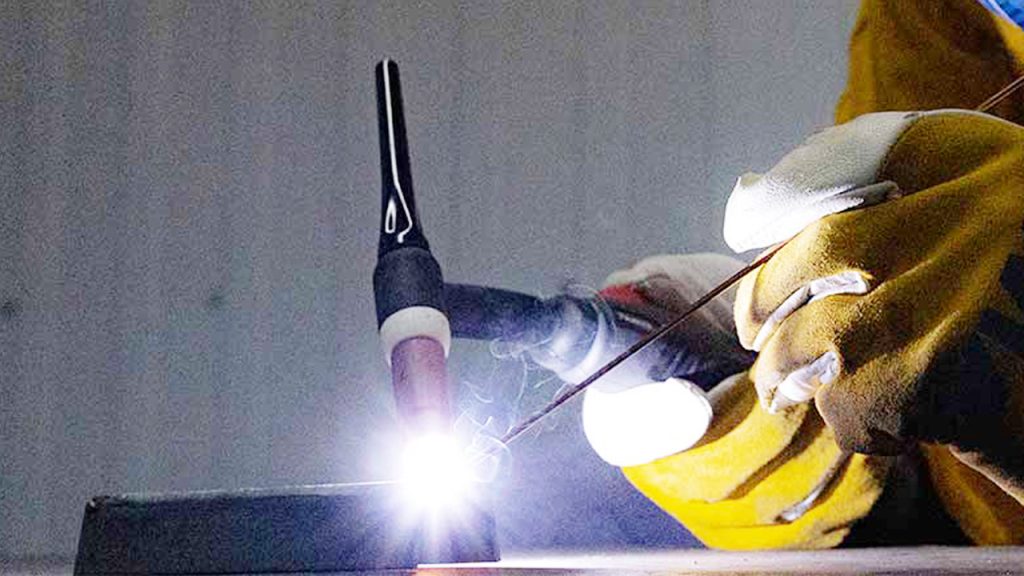
Welding and brazing are popular metal-joining techniques. Both are essential in various industries.
But what sets them apart? Welding and brazing each serve distinct purposes. Welding fuses metals by melting them, creating a strong bond. Brazing, on the other hand, joins metals using a filler without melting the base materials. Understanding these differences is crucial.
It helps in choosing the right technique for your project. This blog will explore the key distinctions between welding and brazing. By the end, you’ll know which method suits your needs better. Let’s dive in and uncover the specifics of these two vital processes.
Credit: blog.red-d-arc.com
Introduction To Welding And Brazing
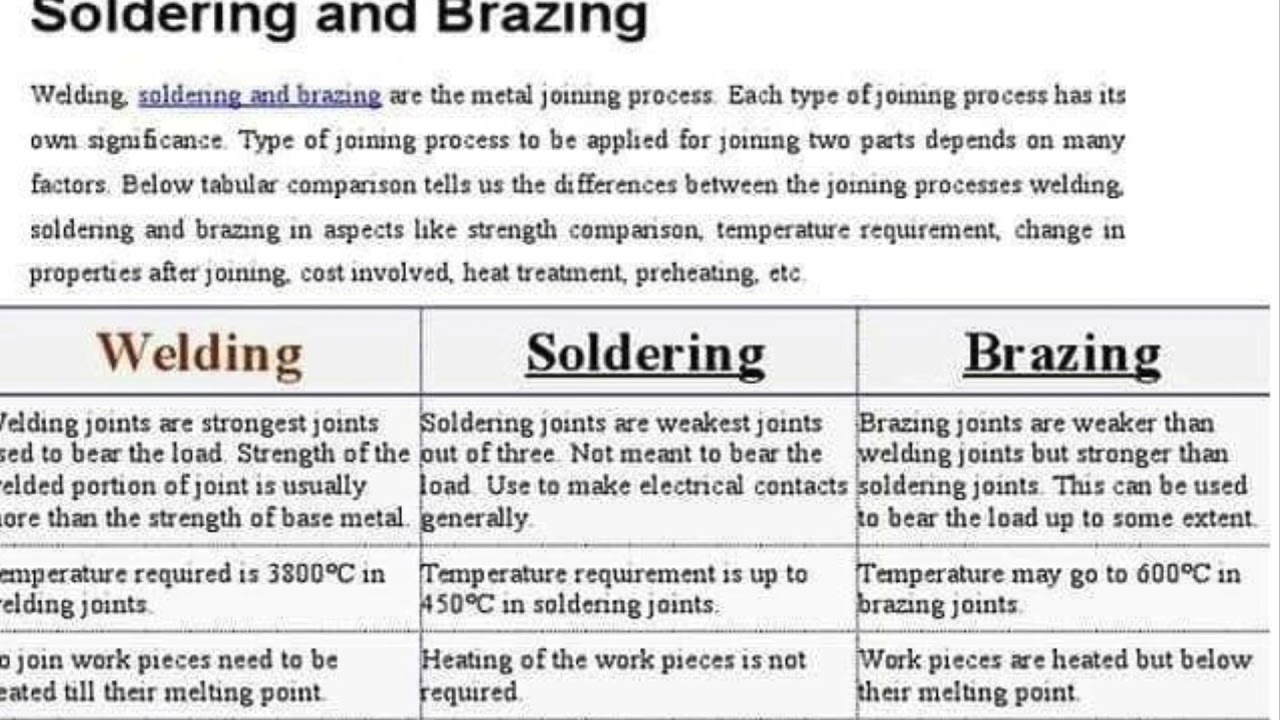
Welding and brazing join metals but differ in technique. Welding melts base metals, while brazing uses a filler without melting the base. Each method serves unique purposes in metal fabrication.
Welding and brazing are two key techniques in the world of metal joining. They both serve essential roles in various industries. While they might seem similar, they are quite different.Brief Overview
Welding is a process that joins metals by melting them together. It creates a strong bond. The melted parts cool to form a solid joint. Heat or pressure, or both, can be used. Brazing, on the other hand, does not melt the base metals. It uses a filler metal with a lower melting point. The filler metal flows into the joint and bonds the pieces. This creates a strong connection without melting the base metals.Importance In Industry
Welding is crucial in construction, manufacturing, and automotive industries. It ensures the strength and durability of structures. Bridges, buildings, and cars rely on welding for safety and stability. Brazing is vital in electronics, plumbing, and HVAC systems. It allows for precise and clean joints. It is used in delicate assemblies where welding might be too aggressive. Both techniques are essential for modern industry needs. “`
Credit: www.linkedin.com
Basic Concepts
When it comes to joining metals, two popular methods are welding and brazing. At first glance, they might seem similar, but they are quite different in their processes and applications. Let’s break down these concepts in a simple and easy-to-understand way.
Definition Of Welding
Welding is a process where two or more metal parts are fused together by melting the base material. Usually, a filler material is added to create a strong joint. In welding, the high temperature is essential to melt the metals. Think of it like using a super-hot glue gun, but instead of glue, it’s molten metal!
Here are some key points about welding:
- High temperatures are used to melt the metals.
- A filler material is often added to strengthen the joint.
- Welded joints are usually stronger than the base metals.
- Common in industries like construction, automotive, and manufacturing.
Definition Of Brazing
Brazing, on the other hand, involves joining metals by melting a filler metal into the joint. The base metals are not melted; instead, the filler metal has a lower melting point and flows between the closely fitted parts. It’s like using a metal solder to glue pieces together.
Here are the main features of brazing:
- The base metals are not melted.
- A filler metal with a lower melting point is used.
- Brazed joints are not as strong as welded joints but are still very durable.
- Used in applications like HVAC systems, plumbing, and electronics.
In a nutshell, while both welding and brazing are used to join metals, they are quite different in their techniques and applications. Welding requires higher temperatures and often results in stronger joints, while brazing is more about precision and is used when the base metals should not be melted.
Processes Involved
Understanding the processes involved in welding and brazing helps distinguish these two metal joining techniques. Both methods have unique steps, tools, and applications. Knowing these can help choose the right approach for different projects.
Welding Techniques
Welding involves melting the base metals. This creates a strong bond. There are several techniques used in welding. Each technique suits different materials and applications.
In arc welding, an electric arc generates heat. This melts the metals. In gas welding, a gas flame melts the metals. This method is often used for thin materials. Another technique is resistance welding. Here, heat is generated by electrical resistance.
Welding needs high temperatures. The process can reach up to 7,000 degrees Fahrenheit. Safety gear is essential. Welders wear helmets, gloves, and protective clothing.
Brazing Methods
Brazing involves joining metals using a filler metal. The base metals do not melt. The filler metal melts and flows into the joint. This creates a bond.
There are different brazing methods. Torch brazing uses a gas flame to melt the filler metal. Furnace brazing heats the assembly in a furnace. Induction brazing uses an electromagnetic field to generate heat.
Brazing works at lower temperatures than welding. It usually ranges from 800 to 2,000 degrees Fahrenheit. This makes it suitable for delicate parts. Brazing also allows joining different metals. It offers more flexibility in material choice.
Credit: www.youtube.com
Materials Used
When it comes to joining metals, two techniques often come into play: welding and brazing. While both processes serve the same purpose, the materials used in each can be quite different. Understanding these differences can help you choose the right method for your project. Let’s dive into the specifics of the materials used in welding and brazing.
Common Welding Materials
Welding involves melting the base metals to fuse them together. The process often requires a filler material, which is typically a metal or alloy. The choice of materials can impact the strength and durability of the weld. Here are some common materials used in welding:
- Steel: One of the most popular choices, steel is versatile and strong. It includes both carbon steel and stainless steel.
- Aluminum: Known for its lightweight and corrosion resistance, aluminum is ideal for projects needing a lighter touch.
- Copper: Great for electrical applications, copper’s excellent conductivity makes it a go-to material.
- Nickel Alloys: Used in high-temperature and corrosive environments, these alloys are tough and durable.
Common Brazing Materials
Brazing, on the other hand, involves melting a filler metal that has a lower melting point than the base metals. This filler metal flows into the joint and bonds the metals together without melting them. Here’s a look at typical materials used in brazing:
- Copper Alloys: Widely used due to their excellent flow properties and strength, copper alloys are suitable for various applications.
- Silver Alloys: Offering high strength and good flow, silver alloys are perfect for delicate or high-stress joints.
- Brass: Often used for its good flow and wetting properties, brass is suitable for joining metals like steel and copper.
- Aluminum Alloys: These are used for joining aluminum parts, providing good corrosion resistance.
In essence, the choice of materials for welding and brazing isn’t just about what you have on hand. It’s about understanding the properties of those materials and how they’ll affect your final product. So next time you’re deciding between welding and brazing, consider the materials at your disposal and the requirements of your project. Happy joining!
Applications
Understanding the applications of welding and brazing is essential. Each method serves distinct purposes in various industries. Let’s explore how these techniques are used in different fields.
Welding Applications
Welding creates strong joints. It is used in construction. Bridges, buildings, and pipelines rely on welded connections. The automotive industry also uses welding. Car frames and parts are welded for durability. Aerospace applications need welding, too. Aircraft structures and components require secure joints. Manufacturing uses welding for machinery and equipment. Shipbuilding depends on welding. Ships and submarines need sturdy welded joints. Welding is crucial in many fields, ensuring strong and reliable connections.
Brazing Applications
Brazing is different from welding. It joins metals without melting them. It is used in HVAC systems. Copper pipes are often brazed for leak-free connections. Electronics use brazing, too. Circuit boards and components are joined with brazed joints. The jewelry industry uses brazing. Delicate pieces need precise, strong bonds. Brazing is common in plumbing. It creates durable, leak-proof joints in pipes. Aerospace uses brazing for heat exchangers. These applications show brazing’s versatility in creating secure, non-melted connections.
Advantages And Disadvantages
When diving into the world of metal joining, it can sometimes feel like navigating a maze. You might wonder, “Should I weld or should I braze?” Understanding the advantages and disadvantages of each method can guide you on the right path. Let’s break it down so it’s as clear as day.
Welding Pros And Cons
Welding is a popular method that involves melting the workpieces and adding a filler material to form a strong joint. But, like a double-edged sword, it has its bright and dark sides.
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
|
|
Brazing Pros And Cons
Brazing, on the other hand, involves joining metals by melting a filler metal into the joint, without melting the base materials. It’s a bit like a chef making a perfect sauce without burning the main dish. Let’s explore its pros and cons.
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
|
|
In conclusion, both welding and brazing have their places in metalworking. Whether you prioritize strength or a neat finish, understanding the advantages and disadvantages of each method will help you choose the right one for your project. What do you think suits your needs best? Don’t hesitate to dive in and try both techniques – you’ll soon find your favorite!
Cost Considerations
When deciding between welding and brazing for your project, it’s important to consider the cost. Both techniques have their advantages and drawbacks, but understanding the financial implications can help you make an informed decision. Let’s break down the costs associated with each method so you can see which one fits your budget better.
Welding Costs
Welding can be a bit of a wallet-drainer, especially for large projects. Here’s why:
- Equipment: The initial investment in welding equipment can be quite high. You need a welding machine, protective gear, and consumables like electrodes or wire.
- Materials: The materials needed for welding, such as filler metals, can also be expensive.
- Energy Consumption: Welding machines consume a significant amount of electricity, which adds to the operating costs.
- Labor: Skilled welders often charge a premium due to the technical expertise required.
On the bright side, welding creates strong, durable joints that are often worth the extra cost. If you’re working on something that needs to withstand a lot of stress, welding might be the best option despite the higher price tag.
Brazing Costs
Brazing, on the other hand, tends to be more budget-friendly. Here’s a quick rundown:
- Equipment: The tools needed for brazing are generally less expensive than welding equipment. A torch and some basic safety gear might be all you need.
- Materials: The filler metals used in brazing, such as brass or silver alloys, can be less costly than those used in welding.
- Energy Consumption: Brazing typically requires less energy, making it cheaper to operate.
- Labor: While still requiring skill, brazing is often simpler and can be done by less specialized workers, reducing labor costs.
However, while brazing is easier on the pocket, it may not be suitable for all projects. The joints created by brazing are not as strong as those made by welding and might not hold up under extreme conditions.
So, what’s the takeaway? If you’re looking for the strongest possible joints and are willing to invest more upfront, welding might be your go-to. But if you’re working on a project with less demanding strength requirements, brazing can save you some cash. In the end, the choice between welding and brazing will depend on your specific needs and budget. Happy fabricating!
Expert Opinions
Welding and brazing join metals but differ in technique and temperature. Welding melts base metals, while brazing uses a filler without melting them. Both methods have unique applications and strengths.
Welding and brazing are vital metal joining processes. They each have unique benefits and applications. To better understand these differences, we turn to expert opinions. Experts from various industries share their insights, shedding light on key distinctions.Industry Perspectives
Experts from the automotive industry prefer welding for its strength. In contrast, professionals from the HVAC sector often choose brazing for its precision. The aerospace industry values welding for its durability under stress. On the other hand, the electronics industry favors brazing for its low-temperature process. Each industry has specific needs, and experts select the process that best meets those requirements.Future Trends
Experts predict advancements in both welding and brazing technologies. Welding may see more automation and improved safety measures. Brazing could benefit from new filler materials and eco-friendly fluxes. Both processes may become more efficient and environmentally friendly. Experts agree that ongoing research will drive these future trends. “`Frequently Asked Questions
Why Would You Braze Instead Of Weld?
Brazing joins metals at lower temperatures, reducing the risk of warping. It also allows for joining dissimilar metals.
What Is The Major Advantage That Brazing Has Over Welding?
Brazing joins dissimilar metals without melting them, preserving their integrity. It creates strong, leak-proof joints suitable for thin materials.
Is Braze Welding Strong?
Yes, braze welding is strong. It creates durable joints by bonding metals using a filler material. The strength depends on proper technique and materials.
When Would You Use Brazing?
Use brazing for joining dissimilar metals, creating strong joints, or when working with thin-walled components. Ideal for precise, leak-proof connections.
Conclusion
Welding and brazing each serve unique purposes in metalwork. Welding fuses metals directly, creating strong joints. Brazing, on the other hand, uses a filler to bond pieces. It works at lower temperatures. Choose welding for heavy-duty tasks. Opt for brazing for delicate or dissimilar metals.
Both techniques require skill and proper tools. Understanding their differences helps in selecting the right method. This knowledge ensures durable and effective results.

