Welding and fabrication are often confused. They are related but distinct processes in metalwork.
Understanding the difference is crucial for many industries. Welding focuses on joining materials, often metals, by melting them together. Fabrication, on the other hand, involves creating structures or products from raw materials, not just joining them. Knowing these differences can help you choose the right process for your project.
This blog post will clarify what sets welding and fabrication apart. It will guide you through their unique roles, methods, and applications. By the end, you’ll have a clear understanding of each process and their importance in various fields.
Introduction To Welding And Fabrication
Welding and fabrication are crucial processes in various industries. They are essential in construction, manufacturing, and many other fields. Understanding these processes can help in choosing the right one for your needs. This introduction will help you grasp the basics of welding and fabrication.
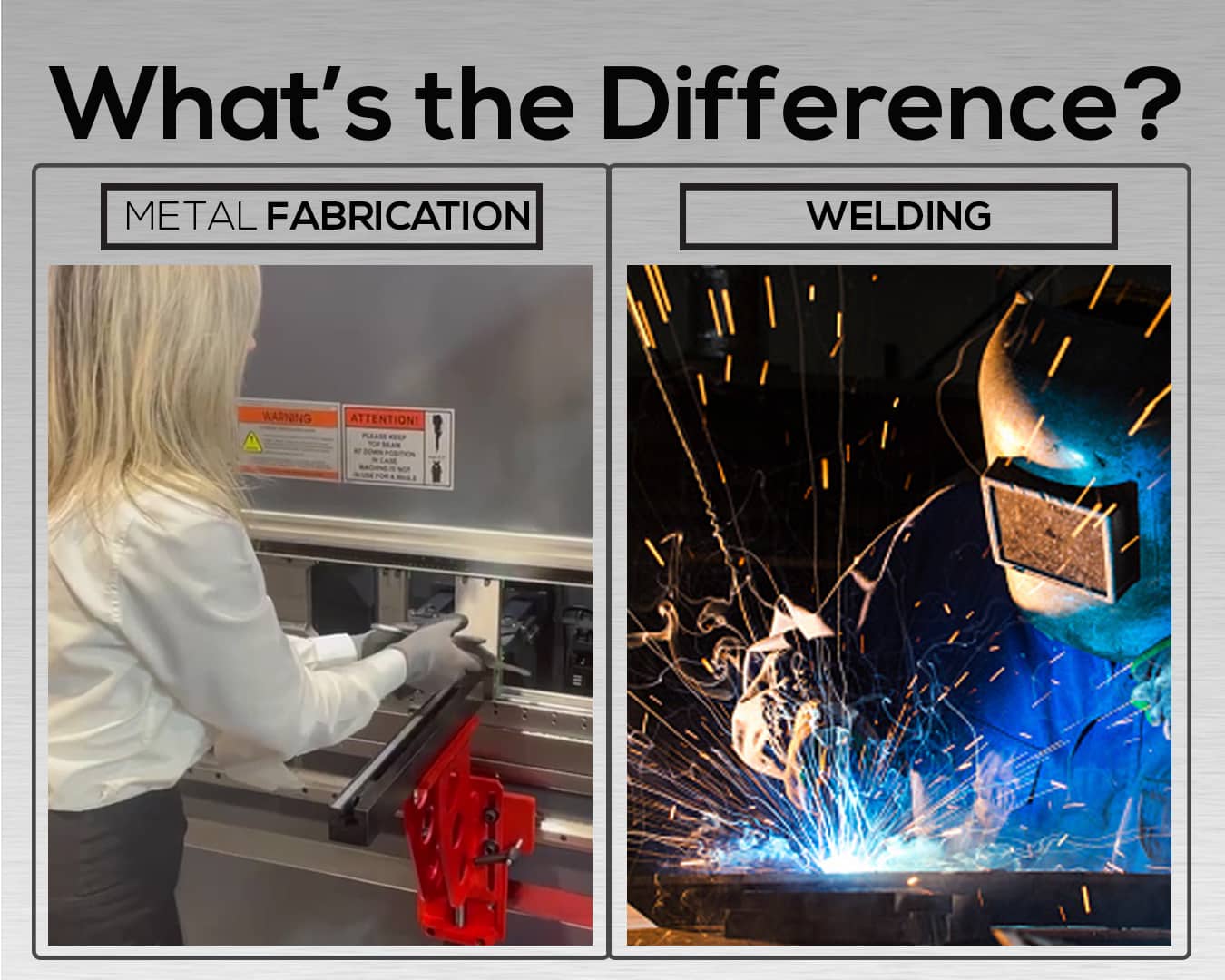
Defining Welding
Welding is a process of joining two or more materials. It often involves metals or thermoplastics. Welders use high heat to melt the parts together. Once cooled, the materials form a strong bond. Different welding techniques exist, such as MIG, TIG, and stick welding. Each technique has its own benefits and applications. Welding is commonly used in construction, automotive, and shipbuilding industries.
Defining Fabrication
Fabrication refers to the process of creating products from raw materials. It involves cutting, bending, and assembling. Unlike welding, fabrication is not just about joining materials. It also includes designing and shaping components. Fabrication can involve various materials, including metals, plastics, and composites. This process is essential in creating complex structures and machinery.
Core Differences
Welding and fabrication are terms often used interchangeably. However, they are not the same. Understanding their core differences helps you appreciate the unique skills and processes each involves. Let’s dive in and uncover what sets them apart.
Process Involved
The processes in welding and fabrication are different. Welding is a part of the fabrication process but is not the whole story.
- Welding: This involves joining two or more pieces of metal together by heating them until they melt and fuse. Think of it as gluing, but with heat instead of adhesive. Common welding techniques include MIG, TIG, and stick welding.
- Fabrication: Fabrication is a broader term. It covers the entire process of building metal structures, from cutting and shaping to assembling. It includes welding as well as other methods like cutting, bending, and assembling.
Skills Required
The skills needed for welding are more specialized compared to those for fabrication.
- Welding Skills: A welder needs to be precise and steady. They must understand different welding techniques and know how to handle the equipment safely. It’s a bit like being a surgeon, but for metal.
- Fabrication Skills: Fabricators need a wider skill set. They must know how to cut, bend, and assemble metal parts. It’s akin to being an architect and builder rolled into one. They need to read blueprints and have a good eye for detail.
In summary, while welding is a part of fabrication, it requires a more focused set of skills. Fabrication, on the other hand, involves a broader range of activities and skills. Understanding these differences can help you appreciate the craftsmanship involved in creating metal structures.
Tools And Equipment
When diving into the world of metal work, understanding the right tools and equipment is crucial. Whether you are welding or fabricating, the tools you use can make or break your project. In this section, we’ll explore the essential tools and equipment that differentiate welding from fabrication. Buckle up, and let’s delve into the nuts and bolts of these two fascinating fields!
Welding Tools
Welding involves joining metals together, usually by melting the parts and adding a filler material. Here are some of the key tools you’ll need:
- Welding Machine: This is the heart of the operation. It generates the heat needed to melt the metals.
- Welding Helmet: Safety first! A helmet protects your eyes and face from sparks and intense light.
- Electrodes: These are the materials that carry the current to the welding point.
- Angle Grinder: Helps clean the metal surfaces before welding.
- Clamps: Keeps your workpieces steady while you weld.
Using these tools correctly ensures strong, clean welds. Ever tried welding without a clamp? It’s like trying to write without holding your pen—messy and frustrating!
Fabrication Tools
Fabrication, on the other hand, is all about cutting, shaping, and assembling metal parts. Think of it as metal origami. Here are the must-have tools:
- Metal Shears: Perfect for cutting metal sheets with precision.
- Press Brake: This machine helps bend metal sheets into various angles.
- Drill Press: Essential for creating holes with exact sizes and positions.
- Measuring Tools: Tools like calipers and tape measures ensure your pieces fit together perfectly.
- Band Saw: Ideal for cutting thicker metal pieces straight and clean.
Imagine trying to fit together a puzzle with pieces that don’t match up. That’s what fabrication would be like without precise tools!
To sum it up, both welding and fabrication require a distinct set of tools tailored to their specific needs. While welding focuses on joining metals, fabrication is about shaping and assembling them. Understanding these tools will set you on the right path to mastering the art of metal work.

Credit: primesourceco.com
Applications And Uses
When it comes to working with metal, two commonly confused terms are welding and fabrication. Although they are related, they serve different purposes and are used in different contexts. In this section, we’ll explore the various applications and uses of welding and fabrication to better understand their unique roles in various industries.
Common Welding Applications
Welding is a process that joins materials, usually metals or thermoplastics, by causing fusion. Here are some common applications:
- Automotive Industry: Welding is essential in manufacturing cars. It is used to join parts of the car body, chassis, and other components. Ever wondered how your car stays in one piece? That’s welding magic!
- Construction: In construction, welding is used to build structures such as bridges, buildings, and pipelines. Without welding, our skylines would look very different.
- Shipbuilding: Ships and submarines require strong, durable joins. Welding ensures that these massive structures can withstand the pressure and harsh conditions of the sea.
- Aerospace: In aerospace, welding is used to create rockets, airplanes, and space shuttles. Precision and strength are crucial in this industry.
- Manufacturing: Many everyday items, from kitchen appliances to machinery, are made using welding techniques.
Common Fabrication Applications
Fabrication involves creating metal structures by cutting, bending, and assembling processes. Here are some typical uses:
- Custom Metal Work: Need a unique metal piece for a specific job? Fabrication is your go-to. It allows for creating custom parts and structures based on precise specifications.
- Industrial Equipment: Fabrication is used to build heavy machinery and industrial equipment. Think of factories filled with customized machines – that’s fabrication at work.
- Architectural Designs: Fancy a bespoke metal staircase or railing? Architectural fabrication brings artistic visions to life with metal.
- Commercial Products: Many products we use daily, from office furniture to kitchen cabinets, are products of fabrication.
- Repair and Maintenance: Fabrication is also crucial in repairing and maintaining existing metal structures and machinery. It ensures longevity and functionality.
To sum up, while welding and fabrication may seem similar, they play distinct roles in metalworking. Welding focuses on joining materials, while fabrication is about creating and assembling. Each has its unique applications, making them both indispensable in various industries.
Materials Used
Understanding the materials used in welding and fabrication is crucial for anyone involved in metalworking. Each process requires specific materials to ensure the best results. While both welding and fabrication may involve working with metals, the types of materials used can vary significantly. Let’s delve deeper into the materials used in welding and fabrication.
Materials For Welding
Welding often involves metals like steel, aluminum, and stainless steel. These metals are popular due to their strength and durability. Welders also use filler materials. These materials help join metal pieces together. Common fillers include welding rods and wires. Different types of filler materials are used for different metals. For instance, aluminum requires specific fillers for a strong weld. Welders also use flux. This material helps prevent oxidation during the welding process.
Materials For Fabrication
Fabrication uses a broader range of materials. Metals like steel, aluminum, and brass are common. Fabricators also work with non-metal materials. These include plastics, glass, and wood. Each material has unique properties. This means different techniques are needed for each one. Fabricators often use sheets, bars, and tubes of these materials. They cut, bend, and shape them into the desired form. The choice of material depends on the project requirements. Strength, weight, and appearance are key factors in this choice.

Credit: www.knowltonindustrialsteel.com
Challenges Faced
Every profession has its hurdles, and welding and fabrication are no exceptions. Whether you’re joining metals or crafting structures, each task brings its own set of challenges. Let’s dive into what makes these jobs tough and how professionals overcome these obstacles.
Welding Challenges
Welding might seem like a straightforward task, but it’s far from it. Here are some of the common challenges welders face:
- Heat Management: Controlling the heat is crucial. Too much heat can warp the metal, while too little might not create a strong bond.
- Safety Hazards: Welders deal with intense light, fumes, and hot materials. Proper gear and ventilation are a must.
- Precision: A steady hand and a sharp eye are needed to ensure the weld is clean and strong. Mistakes can lead to weak joints.
- Material Types: Different metals have different properties. Welders need to know how each type reacts to heat and pressure.
Fabrication Challenges
Fabrication involves turning raw materials into finished products. This process is complex and requires a range of skills. Here are some common hurdles in fabrication:
- Design Accuracy: Following blueprints and specifications to the letter is essential. Even a small error can ruin the whole project.
- Material Handling: Large, heavy materials are tough to move and shape. Proper equipment and techniques are needed to handle them safely.
- Assembly: Bringing all the parts together in the right order and ensuring they fit perfectly is a major challenge.
- Quality Control: Every piece must be inspected for flaws. Ensuring high standards can be time-consuming but is necessary for safety and reliability.
In both welding and fabrication, professionals rely on their training, experience, and a bit of ingenuity to tackle these challenges. Next time you see a metal structure or a welded joint, take a moment to appreciate the skill and effort that went into making it!
Safety Considerations
Safety is crucial in both welding and fabrication. Each process involves unique risks that workers must address. Understanding these safety considerations can help create a safer work environment. Below, we will explore the specific safety measures for welding and fabrication.
Welding Safety
Welders face various hazards, including burns, eye damage, and respiratory issues. Wearing protective gear is essential. This includes helmets, gloves, and flame-resistant clothing. Eye protection is vital to prevent arc eye. Proper ventilation helps reduce inhalation of harmful fumes. Training workers on equipment use and safety protocols is important. Regularly inspect tools to ensure they function correctly. Keep a fire extinguisher nearby in case of fire hazards. These steps help maintain a safe welding environment.
Fabrication Safety
Fabrication involves cutting, bending, and assembling metal parts. Workers must use protective gear like gloves and safety glasses. Proper handling of tools and machinery is crucial. Training helps reduce the risk of accidents. Ensure the workspace is clean and organized. This prevents tripping and other injuries. Regular maintenance of equipment is necessary. It ensures tools operate safely and effectively. Follow safety protocols to avoid injuries during fabrication tasks. Workers should be aware of their surroundings and potential hazards. This helps create a safer workplace for everyone.
Credit: www.rmtus.com
Future Trends
The future of welding and fabrication looks promising. Both industries are evolving with new technologies. Understanding these changes can help professionals stay ahead. Let’s explore the future trends in welding and fabrication.
Advancements In Welding
Welding techniques are becoming more efficient. Laser welding is gaining popularity. It provides precision and speed. Robots are also making a big impact. They can perform repetitive tasks without fatigue. This increases productivity and safety.
New materials are being welded. Traditional methods struggled with certain alloys. Modern welding can handle these materials with ease. This opens new possibilities in various industries.
Welding software is another key advancement. These programs help in planning and execution. They ensure accuracy and reduce errors. Welders can now use augmented reality for training. This offers a hands-on experience without risks.
Innovations In Fabrication
Fabrication is seeing many innovations. 3D printing is at the forefront. It allows for complex designs and rapid prototyping. This technology reduces waste and saves time.
Automation is also transforming fabrication. Machines can now perform tasks that required human intervention. This leads to consistent quality and faster production. CNC machines are a prime example. They offer precision and flexibility.
Smart factories are the next big thing. They use IoT devices to monitor and control processes. This leads to better efficiency and reduced downtime. Fabricators can now track every step of production in real-time.
New materials are being developed for fabrication. These materials are lighter yet stronger. They can withstand extreme conditions. This is crucial for industries like aerospace and automotive.
The future of welding and fabrication is exciting. These advancements and innovations are shaping the industry. Professionals need to stay updated to leverage these trends.
Frequently Asked Questions
Is Welding The Same As Fabrication?
No, welding and fabrication are not the same. Welding is a process of joining materials, usually metals. Fabrication involves creating structures or products from raw materials, which may include welding along with other techniques.
What Is A Welder And Fabricator?
A welder joins metal parts using heat. A fabricator shapes and assembles metal structures. Both create and repair metal products.
What Is An Example Of Fabrication?
An example of fabrication is creating a false story about winning a prestigious award to gain admiration.
What Are The 4 Types Of Welding?
The four types of welding are MIG (Metal Inert Gas), TIG (Tungsten Inert Gas), Stick (Shielded Metal Arc), and Flux-Cored Arc welding. These techniques vary in application and material compatibility.
Conclusion
Welding and fabrication serve different purposes in metalwork. Welding joins metal pieces together. Fabrication involves creating metal structures from raw materials. Both are essential in construction and manufacturing. Understanding their differences helps in choosing the right process. Each has unique tools, techniques, and applications.
Mastery of both can enhance project outcomes. Always consider your project needs when deciding. Skilled workers in each field are highly valuable. Knowing these distinctions aids in better planning and execution.

